Cholic acid for primary bile acid synthesis defects: a life-saving therapy allowing a favorable outcome in adulthood
- PMID: 30373615
- PMCID: PMC6206929
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-018-0920-5
Cholic acid for primary bile acid synthesis defects: a life-saving therapy allowing a favorable outcome in adulthood
Abstract
Background: Oral cholic acid (CA) replacement has been shown to be an effective therapy in children with primary bile acid synthesis defects, which are rare and severe genetic liver diseases. To date there has been no report of the effects of this therapy in children reaching adulthood. The aim of the study was to evaluate the long-term effectiveness and safety of CA therapy.
Methods: Fifteen patients with either 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-C27-steroid oxidoreductase (3β-HSD) (n = 13) or Δ4-3-oxosteroid 5β-reductase (Δ4-3-oxo-R) (n = 2) deficiency confirmed by mass spectrometry and gene sequencing received oral CA and were followed prospectively.
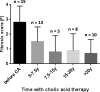
Results: The median age at last follow-up and the median time of follow-up with treatment were 24.3 years (range: 15.3-37.2) and 21.4 years (range: 14.6-24.1), respectively. At last evaluation, physical examination findings and blood laboratory test results were normal in all patients. Liver sonograms were normal in most patients. Mean daily CA dose was 6.9 mg/kg of body weight. Mass spectrometry analysis of urine showed that excretion of the atypical metabolites remained low or traces in amount with CA therapy. Liver fibrosis scored in liver biopsies or assessed by elastography in 14 patients, after 10 to 24 years with CA therapy, showed a marked improvement with disappearance of cirrhosis (median score < F1; range: F0-F2). CA was well tolerated in all patients, including five women having 10 uneventful pregnancies during treatment.
Conclusions: Oral CA therapy is a safe and effective long-term treatment of 3β-HSD and Δ4-3-oxo-R deficiencies and allows affected children to reach adulthood in good health condition without the need for a liver transplantation.
Keywords: AKR1D1; Bile acid; Genetic cholestasis; HSD3B7.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. For the treatment period from 1993 to August 2007, the study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Bicêtre Hospital (Comité de Protection des Personnes, Hôpital Bicêtre, Le Kremlin-Bicêtre, France) and written informed consent was obtained from parents prior to enrollment, as previously reported [14]. Since August 2007 to September 2013, patients benefited from a “Autorisation Temporaire d’Utilisation” delivered for each patient by the “Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé (France)”. Thereafter, the European Commission granted a marketing authorisation valid throughout the European Union for Orphacol on September 2013 [21]. Therefore, for the 10 year period from August 2007 to 2017 which represents the basis of the study, consent to participate was not needed.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
EJ consulted for laboratory CTRS (France). EG received support for travel from CTRS, Alexion, Spindler Mayoli, Albireo. The other authors reported no conflict of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Clayton PT, Leonard JV, Lawson AM, Setchell KD, Andersson S, Egestad B, et al. Familial giant cell hepatitis associated with synthesis of 3 beta, 7 alpha-dihydroxy-and 3 beta,7 alpha, 12 alpha-trihydroxy-5-cholenoic acids. J Clin Invest. 1987;79:1031–1038. doi: 10.1172/JCI112915. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Setchell KD, Suchy FJ, Welsh MB, Zimmer-Nechemias L, Heubi J, Balistreri WF. Delta 4-3-oxosteroid 5 beta-reductase deficiency described in identical twins with neonatal hepatitis. A new inborn error in bile acid synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1988;82:2148–2157. doi: 10.1172/JCI113837. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cheng JB, Jacquemin E, Gerhardt M, Nazer H, Cresteil D, Heubi JE, et al. Molecular genetics of 3beta-hydroxy-Delta5-C27-steroid oxidoreductase deficiency in 16 patients with loss of bile acid synthesis and liver disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:1833–1841. doi: 10.1210/jc.2002-021580. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

