Exploring qualitative methods reported in registered trials and their yields (EQUITY): systematic review
- PMID: 30373646
- PMCID: PMC6206926
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-018-2983-y
Exploring qualitative methods reported in registered trials and their yields (EQUITY): systematic review
Abstract
Background: The value of qualitative methods within trials is widely recognised, but their full potential is not being realised. There are also issues with the visibility, recognition and reporting of qualitative methods in trials. To identify potential improvements in qualitative research within trials, we need to study trials that have included qualitative methods. We aimed to explore the frequency of reporting qualitative methods in registered trials, the types of trials using qualitative methods and where in the world these trials were conducted.
Methods: We included registries if they were searchable using keywords and held summaries of trials rather than listing reports or publications. We searched the included registries from the first available record in 1999 to the end of 2016 for the term 'qualitative'. We included trials only if we could confirm that they used qualitative methods through documented use of qualitative data collection and analysis in the registry summary. We analysed registered trials reporting the use of qualitative methods by: year registered, the country responsible for overseeing governance of the trial and the type of trial intervention (categorised as surgical, medical device, behavioural, drug or other).
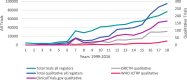
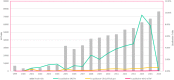
Results: We included three registries: ClinicalTrials.gov, the International Standard Randomised Controlled Trial Number Registry (ISRCTN) and the World Health Organisation International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (WHO ICTRP). A total of 615,311 trials appear in these three registries from 1999 until the end of 2016. Numbers differed across registries with the WHO ICTRP the largest (366,753 trials), ClinicalTrials.gov the second largest (233,277) and ISRCTN the smallest (15,301). Of these registered trials, we confirmed that 1492 (0.24%) reported using qualitative methods. The ISRCTN contributed the highest percentage of trials reported as using qualitative methods (3.4%); in contrast, ClinicalTrials.gov reported 0.3% and WHO ICTRP reported 0.03%. The number and percentage of trials reported to use qualitative methods increased over time from 0 (0.0%) in 1999 to 285 (0.38%) in 2016. Trials reported as using qualitative methods originated from 52 countries across the world. Most were in Western higher-income countries: 38% in the United Kingdom and 28% in the United States. Most registered trials reported as using qualitative methods evaluated behavioural (39%) or other interventions with many fewer trials evaluating drugs (5%), medical devices (5%) or surgical interventions (4%).
Conclusion: The reported use of qualitative methods in registered trials has increased over time and worldwide. They are reportedly more frequent in high-income countries and in trials of behavioural and other interventions. Trialists and other stakeholders need to recognise the benefits of using qualitative methods in surgical, device and drug trials, and trials conducted in poorer countries. Moreover, they should seriously consider using qualitative methods in these trials.
Keywords: Humans; Income; Qualitative research; Randomised controlled trial; Registries; Research design; Research support.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not needed for a systematic review.
Consent for publication
Not needed for a systematic review.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

