The 5-HT2A Receptor (5-HT2AR) Regulates Impulsive Action and Cocaine Cue Reactivity in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats
- PMID: 30373886
- PMCID: PMC6290084
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.118.251199
The 5-HT2A Receptor (5-HT2AR) Regulates Impulsive Action and Cocaine Cue Reactivity in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats
Abstract
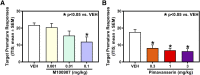
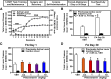
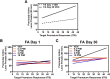
Impulsivity and the attentional orienting response to cocaine-associated cues (cue reactivity) promote relapse in cocaine-use disorder (CUD). A time-dependent escalation of cue reactivity (incubation) occurs during extended, forced abstinence from cocaine self-administration in rats. The investigational serotonin (5-HT) 5-HT2A receptor (5-HT2AR) antagonist/inverse agonist M100907 suppresses impulsive action, or the inability to withhold premature responses, and cocaine-seeking behaviors. The present preclinical study was designed to establish the potential for repurposing the Food and Drug Administration-approved selective 5-HT2AR antagonist/inverse agonist pimavanserin as a therapeutic agent to forestall relapse vulnerability in CUD. In male Sprague-Dawley rats, pimavanserin suppressed impulsive action (premature responses) measured in the 1-choice serial reaction time (1-CSRT) task, similarly to M100907. We also used the 1-CSRT task to establish baseline levels of impulsive action before cocaine self-administration and evaluation of cue reactivity (lever presses reinforced by the discrete cue complex previously paired with cocaine delivery). We observed an incubation of cocaine cue reactivity between day 1 and day 30 of forced abstinence from cocaine self-administration. Baseline levels of impulsive action predicted incubated levels of cocaine cue reactivity in late abstinence. We also found that baseline impulsive action predicted the effectiveness of pimavanserin to suppress incubated cue reactivity in late abstinence from cocaine self-administration at doses that were ineffective in early abstinence. These data suggest that integration of clinical measures of impulsive action may inform refined, personalized pharmacotherapeutic intervention for the treatment of relapse vulnerability in CUD.
U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Blockade of the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor suppresses cue-evoked reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in a rat self-administration model.Behav Neurosci. 2009 Apr;123(2):382-96. doi: 10.1037/a0014592. Behav Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19331461 Free PMC article.
-
Individual Differences in Impulsive Action Reflect Variation in the Cortical Serotonin 5-HT2A Receptor System.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015 Jul;40(8):1957-68. doi: 10.1038/npp.2015.46. Epub 2015 Feb 10. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25666313 Free PMC article.
-
Synergism between a serotonin 5-HT2A receptor (5-HT2AR) antagonist and 5-HT2CR agonist suggests new pharmacotherapeutics for cocaine addiction.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013 Jan 16;4(1):110-21. doi: 10.1021/cn300072u. Epub 2012 Aug 11. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23336050 Free PMC article.
-
Incubation of cocaine cue reactivity associates with neuroadaptations in the cortical serotonin (5-HT) 5-HT2C receptor (5-HT2CR) system.Neuroscience. 2016 Jun 2;324:50-61. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.052. Epub 2016 Feb 27. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26926963 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of cocaine relapse-like behaviors upon pimavanserin and lorcaserin co-administration.Neuropharmacology. 2020 May 15;168:108009. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108009. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32145488 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Heightened cocaine-seeking in male rats associates with a distinct transcriptomic profile in the medial prefrontal cortex.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 14;13:1022863. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1022863. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36588704 Free PMC article.
-
Psilocybin reduces heroin seeking behavior and modulates inflammatory gene expression in the nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex of male rats.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 1:2024.05.28.596205. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.28.596205. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Mol Psychiatry. 2025 May;30(5):1801-1816. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02788-y. PMID: 38854027 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The role of brain serotonin signaling in excessive alcohol consumption and withdrawal: A call for more research in females.Neurobiol Stress. 2024 Feb 20;30:100618. doi: 10.1016/j.ynstr.2024.100618. eCollection 2024 May. Neurobiol Stress. 2024. PMID: 38433994 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the 5-HT2C receptor drugs RO 60-0175, WAY 161503 and mirtazepine in a preclinical model of comorbidity of depression and cocaine addiction.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Feb;75(1):99-118. doi: 10.1007/s43440-022-00428-2. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36374478 Free PMC article.
-
Pimavanserin and Lorcaserin Attenuate Measures of Binge Eating in Male Sprague-Dawley Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Dec 7;9:1424. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01424. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30581386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anastasio NC, Gilbertson SR, Bubar MJ, Agarkov A, Stutz SJ, Jeng Y, Bremer NM, Smith TD, Fox RG, Swinford SE, et al. (2013) Peptide inhibitors disrupt the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor interaction with phosphatase and tensin homolog to allosterically modulate cellular signaling and behavior. J Neurosci 33:1615–1630. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anastasio NC, Stutz SJ, Fox RG, Sears RM, Emeson RB, DiLeone RJ, O’Neil RT, Fink LH, Li D, Green TA, et al. (2014b) Functional status of the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor (5-HT2CR) drives interlocked phenotypes that precipitate relapse-like behaviors in cocaine dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 39:370–382. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

