Expression of Micro-RNA-492 (MiR-492) in Human Cervical Cancer Cell Lines is Upregulated by Transfection with Wild-Type P53, Irradiation, and 5-Fluorouracil Treatment In Vitro
- PMID: 30374014
- PMCID: PMC6354641
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.911585
Expression of Micro-RNA-492 (MiR-492) in Human Cervical Cancer Cell Lines is Upregulated by Transfection with Wild-Type P53, Irradiation, and 5-Fluorouracil Treatment In Vitro
Abstract
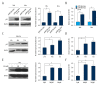
BACKGROUND The status of p53 is critical to the chemoradiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells. Wild-type p53 is essential to orchestrate the cellular response to cytotoxic stimuli. Our previous data illustrated that cervical cancer patients whose specimens overexpressed microR-492 (miR-492) were highly sensitive to concurrent chemoradiation. Although p53 activation has been reported to upregulate miR-492 by a miRNA profiling assay in lung cancer cells, the transcriptional regulation of miR-492 in cervical cancer cells remains poorly understood. Therefore, we aimed to decipher the relationship between p53 and miR-492 in cervical cancer cells. MATERIAL AND METHODS The expression of p53 and miR-492 in cervical cancer cell lines was measured by western blot and real-time PCR. After cells were transfected with wild-type p53 plasmid or were treated by irradiation and 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), the expression changes of p53 as well as miR-492 were examined by western blot and real-time PCR. The putative p53 binding site of miR-492 was first analyzed by bioinformatics tools, then validated by chromatin immunoprecipitation and dual-luciferase reporter assays. RESULTS We found that miR-492 was upregulated in cells with wild-type p53 compared to cells with mutant p53. Transfection of wild-type p53 plasmid or treatments with cytotoxic reagents including irradiation and 5-FU all induced miR-492 overexpression. Bioinformatics analysis and experimental validations further proved p53 interacted with miR-492 promoter directly. CONCLUSIONS In cervical cancer cells, p53 activated miR-492 expression transcriptionally.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Musashi-2, a novel oncoprotein promoting cervical cancer cell growth and invasion, is negatively regulated by p53-induced miR-143 and miR-107 activation.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Oct 26;36(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0617-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 29073938 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of miR-22, a tumor suppressor in cervical cancer, by human papillomavirus 16 E6 via a p53/miR-22/HDAC6 pathway.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 31;13(10):e0206644. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206644. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30379969 Free PMC article.
-
Glucocorticoid regulation of a novel HPV-E6-p53-miR-145 pathway modulates invasion and therapy resistance of cervical cancer cells.J Pathol. 2012 Oct;228(2):148-57. doi: 10.1002/path.3997. Epub 2012 Apr 18. J Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22287315
-
MicroRNA in cervical cancer: OncomiRs and tumor suppressor miRs in diagnosis and treatment.ScientificWorldJournal. 2014 Jan 2;2014:178075. doi: 10.1155/2014/178075. eCollection 2014. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014. PMID: 24516357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative p53, micro-RNA and Cathepsin Protease Co-Regulatory Expression Networks in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 20;12(11):3454. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113454. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33233599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating miRNAs in Serum as Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Front Genet. 2021 Jul 9;12:673926. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.673926. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34306018 Free PMC article.
-
miR-492 Promotes Cancer Progression by Targeting GJB4 and Is a Novel Biomarker for Bladder Cancer.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Dec 24;12:11453-11464. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S223448. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 31920334 Free PMC article.
-
miR‑34c‑5p targets Notch1 and suppresses the metastasis and invasion of cervical cancer.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Feb;23(2):120. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2020.11759. Epub 2020 Dec 10. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33300051 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a novel circular RNA as an independent prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia.BMC Med. 2021 Feb 1;19(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01898-y. BMC Med. 2021. PMID: 33517886 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-139-5p-ZEB1 is a Molecular Regulator of Growth, Invasion, and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Cervical Cancer.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Dec 10;12:12723-12733. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S267634. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 33328767 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86. - PubMed
-
- Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–32. - PubMed
-
- Koh WJ, Greer BE, Abu-Rustum NR, et al. Cervical Cancer, Version 2.2015 Featured Updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2015;13(4):395–404. quiz 404. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

