Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Deposition Disease in Young Patients: Two Case Reports
- PMID: 30375521
- PMCID: PMC6190932
- DOI: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2017.6015
Calcium Pyrophosphate Dihydrate Deposition Disease in Young Patients: Two Case Reports
Abstract
Calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPDD) is a type of arthritis caused by the deposition of calcium pyrophosphate crystals, and may present as either acute or chronic arthritis. Development of CPPD crystal deposition disease in young people may be associated with metabolic diseases such as hemochromatosis, hyperparathyroidism, hypomagnesemia, Wilson's disease, hypothyroidism, gout, acromegaly, and X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Therefore, investigations for a predisposing metabolic condition are advised in young-onset polyarticular CPPD crystal deposition disease. In this article, we report two young patients who were investigated for recurrent joint pain due to CPPD disease.
Keywords: Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate; chondrocalcinosis; pseudogout.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The author declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
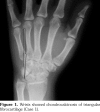
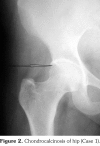
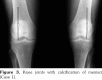
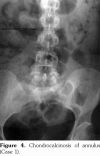
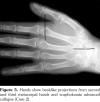
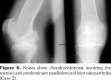
References
-
- McCarty DJ. Calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease--1975. Arthritis Rheum. 1976;19:275–285. - PubMed
-
- Hughes AE, McGibbon D, Woodward E, Dixey J, Doherty M. Localisation of a gene for chondrocalcinosis to chromosome 5p. Hum Mol Genet. 1995;4:1225–1228. - PubMed
-
- Richette P, Bardin T, Doherty M. An update on the epidemiology of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystal deposition disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48:711–715. - PubMed
-
- Netter P, Bardin T, Bianchi A, Richette P, Loeuille D. The ANKH gene and familial calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate deposition disease. Joint Bone Spine. 2004;71:365–368. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
