Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Mean Platelet Volume as Inflammatory Indicators in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Nephritis
- PMID: 30375538
- PMCID: PMC6190939
- DOI: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2017.5886
Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Mean Platelet Volume as Inflammatory Indicators in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Nephritis
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to evaluate the role of neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and mean platelet volume (MPV) as activation and inflammatory markers in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients with nephritis.
Patients and methods: A total of 108 SLE patients (8 males, 100 females; mean age 35.3±10.2 years; range 16 to 64 years) including 78 patients with renal involvement (8 males, 70 females; mean age 33.9±10.6 years; range 16 to 64 years) (SLEn+ group) and 30 patients without renal involvement (30 females; mean age 39.1±8.2 years; range 22 to 55 years) (SLEn- group) were included in this retrospective study. All patients' clinical characteristics and laboratory data which include erythrocyte sedimentation rate, C-reactive protein, white blood counts, neutrophil counts, lymphocyte counts, platelet counts, and MPV levels were obtained from medical records. The laboratory data at the highest proteinuria periods of the patients with renal involvement were recorded.
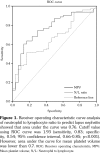
Results: Mean MPV (SLEn+ =9.1±2.2, SLEn- =7.9±1.2, p=0.001) and NLR (SLEn+ =5.9±5.9, SLEn- =2.6±2.5, p<0.001) values were significantly higher in lupus nephritis group. Besides, a positive correlation between NLR and C-reactive protein was found in lupus nephritis group (r=1.97, p=0.045). Based on receiver operating characteristic curve with area under the curve of 0.76, cutoff NLR value of 1.93 had 83% sensitivity and 54% specificity [95% confidence interval, 0.66-0.85] in differentiating SLE patients with or without nephritis.
Conclusion: Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and MPV may be discriminative for lupus nephritis. Also, NLR may be a predictor of lupus nephritis. Both MPV and NLR values may be affected by a great number of factors; therefore, further prospective studies are needed to evaluate the use of these parameters in SLE.
Keywords: Mean platelet volume; nephritis; neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jul 25;24(1):170. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01438-5. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39052098 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were useful markers in assessment of inflammatory response and disease activity in SLE patients.Mod Rheumatol. 2016;26(3):372-6. doi: 10.3109/14397595.2015.1091136. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Mod Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26403379
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte and platelet to lymphocyte ratios in systemic lupus erythematosus: Relation with disease activity and lupus nephritis.Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 2020 Jul-Aug;16(4):255-261. doi: 10.1016/j.reuma.2018.07.008. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). 2020. PMID: 30166230 English, Spanish.
-
Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in systemic lupus erythematosus disease: a retrospective study.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jul 15;8(7):11026-31. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26379900 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio and platelet to lymphocyte ratio in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and their correlation with activity: A meta-analysis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Nov;76:105949. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105949. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31634817
Cited by
-
Mean Platelet Volume Values May Have not a Predictive Role for the Presence of Nephritis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients.Arch Rheumatol. 2017 May 8;32(4):373-374. doi: 10.5606/ArchRheumatol.2017.6380. eCollection 2017 Dec. Arch Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 29900977 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in systemic lupus erythematosus.Clin Exp Med. 2024 Jul 25;24(1):170. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01438-5. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 39052098 Free PMC article.
-
Low serum C3 level, high neutrophil-lymphocyte-ratio, and high platelet-lymphocyte-ratio all predicted poor long-term renal survivals in biopsy-confirmed idiopathic membranous nephropathy.Sci Rep. 2019 Apr 17;9(1):6209. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-42689-7. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30996263 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Mean Platelet Volume and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Meta-Analysis.Iran J Public Health. 2024 May;53(5):978-987. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v53i5.15578. Iran J Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38912146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond Hemostasis: Platelet Innate Immune Interactions and Thromboinflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 31;23(7):3868. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073868. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35409226 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Domsic RT, Goldman RR, Manzi S. In: Hochberg MC, Silman AC, editors. Rheumatology: Mosby. 4th ed. Mosby: Elsevier; 2008. Systemic lupus eritematozus epidemyology and classification; pp. 1211–1215.
-
- Ruperto N, Hanrahan LM, Alarcón GS, Belmont HM, Brey RL, Brunetta P, et al. International consensus for a definition of disease flare in lupus. Lupus. 2011;20:453–462. - PubMed
-
- Bertsias GK, Tektonidou M, Amoura Z, Aringer M, Bajema I, Berden JH, et al. Joint European League Against Rheumatism and European Renal Association-European Dialysis and Transplant Association (EULAR/ERA-EDTA) recommendations for the management of adult and paediatric lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1771–1782. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
