Association Between Sarcopenic Obesity and Falls in a Multiethnic Cohort of Postmenopausal Women
- PMID: 30375641
- PMCID: PMC6289680
- DOI: 10.1111/jgs.15613
Association Between Sarcopenic Obesity and Falls in a Multiethnic Cohort of Postmenopausal Women
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate associations between sarcopenia, obesity, and sarcopenic obesity and incidence of falls in a racially and ethnically diverse cohort of healthy postmenopausal women.
Design: Prospective cohort study.
Setting: Three Women's Health Initiative (WHI) clinical centers (Tucson-Phoenix, AZ; Pittsburgh, PA; Birmingham, AL).
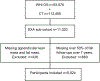
Participants: Postmenopausal women aged 50 to 79 enrolled in the WHI who underwent bone and body composition scans using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry at baseline (N = 11,020).
Measurements: Sarcopenia was defined as the lowest 20th percentile of appendicular lean mass, correcting for height and body fat. Obesity was defined as a body fat percentage greater than 42%. Sarcopenic obesity was defined as co-occurrence of sarcopenia and obesity. The fall outcome was defined as falling 2 or more times in any year during 7 years of follow-up. The risk of falls associated with sarcopenic obesity were analyzed using log binomial regression models stratified according to age and race/ethnicity.
Results: Sarcopenic obesity was associated with greater risk of falls in women aged 50 to 64 (relative risk (RR) = 1.35, 95% confidence interval (CI)=1.17-1.56) and 65 to 79 (RR = 1.21, 95% CI=1.05-1.39). Sarcopenic obesity related fall risk was higher in Hispanic women (RR = 2.40, 95% CI=1.56-3.67) than non-Hispanic white women (RR = 1.24, 95% CI=1.11-1.39).
Conclusion: In a multiethnic cohort of postmenopausal women, sarcopenic obesity-related fall risk was high in women younger than 65 and those age 65 and older. Sarcopenic obesity posed the highest risk for falls in Hispanic women. The findings support identification of causal factors and health disparities in sarcopenic obesity to customize fall prevention strategies and ameliorate this significant public health burden. J Am Geriatr Soc 66:2314-2320, 2018.
Keywords: Women's Health Initiative; falls; obesity; race; sarcopenia.
© 2018, Copyright the Authors Journal compilation © 2018, The American Geriatrics Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment in
-
Effects of Hormone Replacement Therapy on Sarcopenia: Is It Real?J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019 Jun;67(6):1297. doi: 10.1111/jgs.15807. Epub 2019 Jan 30. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019. PMID: 30697703 No abstract available.
References
-
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Ageing 2015 2015;(ST/ESA/SER.A/390). doi:ST/ESA/SER.A/390
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201600002C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100046C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201600001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- NH/NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100001C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services/International
- HHSN268201600018C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201600003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201100004C/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100002C/WH/WHI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201600004C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States