A constructive approach to the epistemological problem of emergence in complex systems
- PMID: 30376579
- PMCID: PMC6207336
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206489
A constructive approach to the epistemological problem of emergence in complex systems
Abstract
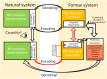
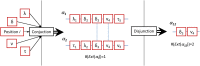
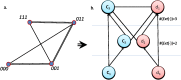
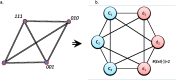
Emergent patterns in complex systems are related with many intriguing phenomena in modern science. One question that has sparked vigorous debates is if difficulties in the modelization of emergent behaviours are a consequence of ontological or epistemological limitations. To elucidate this question, we propose a novel approximation through constructive logic. Under this framework, experimental measurements will be considered conceptual building blocks from which we aim to achieve a description of the microstates ensemble mapping the macroscopic emergent observation. This procedure allow us to have full control of any information loss, thus making the analysis of different systems fairly comparable. In particular, we aim to look for compact descriptions of the constraints underlying a dynamical system, as a necessary a priori step to develop explanatory (mechanistic) models. We apply our proposal to a synthetic system to show that the number and scope of the system's constraints hinder our ability to build compact descriptions, being those systems under global constraints a limiting case in which such a description is unreachable. This result clearly links the epistemological limits of the framework selected with an ontological feature of the system, leading us to propose a definition of emergence strength which we make compatible with the scientific method through the active intervention of the observer on the system, following the spirit of Granger causality. We think that our approximation clarifies previous discrepancies found in the literature, reconciles distinct attempts to classify emergent processes, and paves the way to understand other challenging concepts such as downward causation.
Conflict of interest statement
The author has declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Automated ontology generation framework powered by linked biomedical ontologies for disease-drug domain.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018 Oct;165:117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.08.010. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30337066
-
Causation and evidence-based practice: an ontological review.J Eval Clin Pract. 2012 Oct;18(5):1006-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2012.01908.x. J Eval Clin Pract. 2012. PMID: 22994999 Review.
-
[Dynamic paradigm in psychopathology: "chaos theory", from physics to psychiatry].Encephale. 2001 May-Jun;27(3):260-8. Encephale. 2001. PMID: 11488256 French.
-
Conflicting emergences. Weak vs. strong emergence for the modelling of brain function.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019 Apr;99:3-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2019.01.023. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019. PMID: 30684520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The epistemological-ontological divide in clinical radiology.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2005;116:749-54. Stud Health Technol Inform. 2005. PMID: 16160348
References
-
- Nietzsche F. Thus spoke Zarathustra. Manis J, editor. Hazleton: Pennsylvania State Univerity; 2013.
-
- Emmeche C, Køppe S, Stjernfelt F. Explaining emergence: towards an ontology of levels. Journal for General Philosophy of Science. 1997;28(1):83–117. 10.1023/A:1008216127933 - DOI
-
- Corning PA. The re-emergence of emergence, and the causal role of synergy in emergent evolution. Synthese. 2012;185(2):295–317. 10.1007/s11229-010-9726-2 - DOI
-
- Kim J. Making sense of emergence. Philosophical studies. 1999;95(1):3–36. 10.1023/A:1004563122154 - DOI

