Validity of genus Perostrongylus Schlegel, 1934 with new data on Perostrongylus falciformis (Schlegel, 1933) in European badgers, Meles meles (Linnaeus, 1758): distribution, life-cycle and pathology
- PMID: 30376875
- PMCID: PMC6208079
- DOI: 10.1186/s13071-018-3124-x
Validity of genus Perostrongylus Schlegel, 1934 with new data on Perostrongylus falciformis (Schlegel, 1933) in European badgers, Meles meles (Linnaeus, 1758): distribution, life-cycle and pathology
Abstract
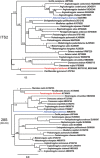
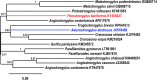
Background: A century of debates on the taxonomy of members of the Metastrongyloidea Molin, 1861 led to many reclassifications. Considering the inconstant genus assignation and lack of genetic data, the main aim of this study was to support the validity of the genus Perostrongylus Schlegel, 1934, previously considered a synonym of Aelurostrongylus Cameron, 1927, based on new molecular phylogenetic data and to understand its evolutionary relationships with other metastrongyloid nematodes.
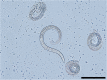
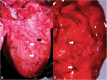
Results: Specimens of lungworm collected from European badgers in Germany, Romania and Bosnia and Herzegovina were morphologically and molecularly (rDNA, cox1) characterized. From a phylogenetic standpoint, Perostrongylus is grouped with high support together with the genera Filaroides van Beneden, 1858 and Parafilaroides Dougherty, 1946 and includes probably two species: Perostrongylus falciformis (Schlegel, 1933), a parasite of Meles meles in Europe and P. pridhami (Anderson, 1962), a parasite of Neovison vison in North America. Perostrongylus and Aelurostrongylus are assigned to different clades. Aelurostrongylus becomes a monotypic genus, with the only species Aelurostrongylus abstrusus (Railliet, 1898). In addition, we provide morphological and morphometric data for the first-stage (L1), second-stage (L2), and third-stage (L3) larvae of P. falciformis and describe their development in experimentally infected Cornu aspersum snails. The pathological and histopathological lesions in lungs of infected European badgers are also described. This is the first record of P. falciformis in Romania.
Conclusions: Molecular phylogenetic and morphological data support the validity of the genus Perostrongylus, most probably with two species, P. falciformis in European badgers and P. pridhami in minks in North America. The two genera clearly belong to two different clades: Perostrongylus is grouped together with the genera Filaroides and Parafilaroides (both in the family Filaroididae Schulz, 1951), whereas Aelurostrongylus belongs to a clade with no sister groups.
Keywords: Aelurostrongylus; European badgers; Metastrongyloidea; Perostrongylus; mustelids.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was performed in accordance with the national and European rules and regulations for research ethics. No live vertebrates were used in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The first report of Aelurostrongylus falciformis (Schlegel, 1933) (Nematoda, Metastrongyloidea) in badger (Meles meles) in Poland.Ann Parasitol. 2017;63(2):117-120. doi: 10.17420/ap6302.94. Ann Parasitol. 2017. PMID: 28822203
-
The first report of Aelurostrongylus falciformis in Norwegian badgers (Meles meles).Acta Vet Scand. 2006 Jun 13;48(1):6. doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-48-6. Acta Vet Scand. 2006. PMID: 16987402 Free PMC article.
-
The first reported case of advanced aelurostrongylosis in Eurasian badger (Meles meles, L. 1758) in Bosnia and Herzegovina: histopathological and parasitological findings.Parasitol Res. 2018 Sep;117(9):3029-3032. doi: 10.1007/s00436-018-5984-6. Epub 2018 Jun 23. Parasitol Res. 2018. PMID: 29934693
-
Current knowledge about Aelurostrongylus abstrusus biology and diagnostic.Ann Parasitol. 2018;64(1):3-11. doi: 10.17420/ap6401.126. Ann Parasitol. 2018. PMID: 29716180 Review.
-
Angiostrongylus vasorum and Aelurostrongylus abstrusus: Neglected and underestimated parasites in South America.Parasit Vectors. 2018 Mar 27;11(1):208. doi: 10.1186/s13071-018-2765-0. Parasit Vectors. 2018. PMID: 29587811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular phylogeny of the Pseudaliidae (Nematoda) and the origin of associations between lungworms and marine mammals.Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2023 Mar 9;20:192-202. doi: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2023.03.002. eCollection 2023 Apr. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2023. PMID: 36969083 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and epidemiological analysis of Perostrongylus falciformis infestation in Irish badgers.Ir Vet J. 2019 Jul 9;72:7. doi: 10.1186/s13620-019-0144-6. eCollection 2019. Ir Vet J. 2019. PMID: 31333818 Free PMC article.
-
Habitat Characteristics as Potential Drivers of the Angiostrongylus daskalovi Infection in European Badger (Meles meles) Populations.Pathogens. 2021 Jun 7;10(6):715. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10060715. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34200340 Free PMC article.
-
DNA Footprints: Using Parasites to Detect Elusive Animals, Proof of Principle in Hedgehogs.Animals (Basel). 2020 Aug 14;10(8):1420. doi: 10.3390/ani10081420. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32823900 Free PMC article.
-
An investigation of Mycobacterium bovis and helminth coinfection in the European badger Meles meles.Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2022 Nov 10;19:311-316. doi: 10.1016/j.ijppaw.2022.11.001. eCollection 2022 Dec. Int J Parasitol Parasites Wildl. 2022. PMID: 36444386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cameron TWM. Studies on three new genera and some little-known species of the nematode family Protostrongylidae Leiper, 1926. J Helminthol. 1927;5:1–24. doi: 10.1017/S0022149X00018472. - DOI
-
- Mueller A. Helminthologisch Mittheilungen. Dtsch Z Sportmed. 1927;17:58–70.
-
- Railliet A. Rectification de la nomenclature d’apres les traveaux recents. Rec Med Vet. 1898;75:171–4.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

