[β2-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor promotes development of GABAA receptors in mouse hippocampal CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons]
- PMID: 30377105
- PMCID: PMC6744193
- DOI: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2018.09.04
[β2-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor promotes development of GABAA receptors in mouse hippocampal CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons]
Abstract
Objective: To explore the role of β2-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (β2-nAChR) in the development of γ- aminobutyric acid A type receptors (GABAA-Rs) in hippocampal CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons of mice.
Methods: The hippocampal CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons were acutely isolated from β2-nAChR gene knockout (β2-KO group) mice. GABA currents in CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons were induced with the selective GABAA-R agonist muscimol and recorded using perforated patch-clamp recording technique. The GABA currents of CA1 and CA3 pyramidal neurons were tested for their equilibrium potentials (EMuss) and kinetic parameters and were compared with the measurements in wild-type mice (WT group).
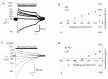
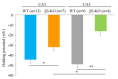
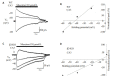
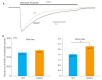
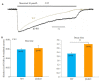
Results: The mean EMus of CA1 neurons (n=7) of β2-KO mice (n=4) was -31.7±3.5 mV, showing an obvious depolarizing shift compared with the WT mice (P < 0.05); the mean EMus of CA3 neurons (n=4) was -16.1±4.6 mV, also showing a depolarizing shift (P < 0.01). The difference in the EMuss between CA3 and CA1 neurons in β2-KO mice, but not in WT mice, was significant (P < 0.05). The GABAA-R desensitization was significantly slowed down in both CA1 and CA3 neurons of β2-KO mice, with decay time of 2.2±0.2 s and 3.2±0.1 s, respectively, significantly longer than those in WT mice (1.6±0.1 s and 2.3±0.1 s, respectively; P < 0.05).
Conclusions: β2-containing nAChRs may promote the functional maturation of GABAA-R in CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cells in mouse hippocampus.
目的: 探讨β2-烟碱型乙酰胆碱受体(β2-nAChR)在海马CA1和CA3锥体神经元的A型γ-氨基丁酸受体(GABAA-R)发育中的作用。
方法: 应用β2-nAChR基因敲除小鼠(β2-KO组)制备急性分离的海马CA1和CA3锥体神经元,应用穿孔膜片钳记录技术记录GABAA-R选择性激动剂蝇蕈醇在CA1和CA3锥体神经元诱导的GABA电流,测试其平衡电位(EMus)和动力学指标,并与野生型小鼠(WT组)进行比较。
结果: β2-KO组小鼠(n=4)CA1锥体神经元(n=7)的EMus为-31.7±3.5 mV,与WT组相比向去极化偏移(P < 0.05);CA3锥体神经元(n=4)的EMus为-16.1±4.6 mV,同样较WT组偏向去极化方向(P < 0.01);与WT组小鼠不同,β2- KO组小鼠CA3和CA1神经元的EMus差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。β2-KO组小鼠CA1和CA3神经元上都显示GABAA-R的失敏显著减慢,衰减时间分别为2.2±0.2 s、3.2±0.1 s(WT组为1.6±0.1 s、2.3±0.1 s,P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。
结论: 含β2的nAChR可能参与促进小鼠海马CA1和CA3锥体细胞中GABAA-R的功能成熟。
Keywords: equilibrium potential of muscimol-induced currents; gene knockout; hippocampus; kinetic indexes; β2-nicotinic acetylcholine receptors; γ-aminobutyric acid A type receptors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synaptic GABA(A) activation inhibits AMPA-kainate receptor-mediated bursting in the newborn (P0-P2) rat hippocampus.J Neurophysiol. 2000 Jan;83(1):359-66. doi: 10.1152/jn.2000.83.1.359. J Neurophysiol. 2000. PMID: 10634879
-
Interferon-γ potentiates GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory currents in rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.J Neuroimmunol. 2019 Dec 15;337:577050. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2019.577050. Epub 2019 Sep 3. J Neuroimmunol. 2019. PMID: 31505410
-
Activation of functional α7-containing nAChRs in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons by physiological levels of choline in the presence of PNU-120596.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 12;5(11):e13964. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0013964. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21103043 Free PMC article.
-
Selective vulnerability of hippocampal CA1 and CA3 pyramidal cells: What are possible pathomechanisms and should more attention be paid to the CA3 region in future studies?J Neurosci Res. 2024 Jan;102(1):e25276. doi: 10.1002/jnr.25276. J Neurosci Res. 2024. PMID: 38284845 Review.
-
Discovering the Intriguing Properties of Extrasynaptic γ-Aminobutyric Acid Type A Receptors.Anesthesiology. 2024 Jun 1;140(6):1192-1200. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000004949. Anesthesiology. 2024. PMID: 38624275 Review.
References
-
- Ntamati NR, Lüscher C. VTA projection neurons releasing GABA and glutamate in the dentate gyrus. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=0935b1e7e5d3da331fdb9e4c129405a5&.... Eneuro. 2016;3(4):116–37. [Ntamati NR, Lüscher C. VTA projection neurons releasing GABA and glutamate in the dentate gyrus[J]. Eneuro, 2016, 3(4):116-37.] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zheng F, Khanna S. Intra-hippocampal tonic inhibition influences formalin pain-induced pyramidal cell suppression, but not excitation in dorsal field CA1 of rat. Brain Res Bull. 2008;77(6):374–81. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.09.004. [Zheng F, Khanna S. Intra-hippocampal tonic inhibition influences formalin pain-induced pyramidal cell suppression, but not excitation in dorsal field CA1 of rat[J]. Brain Res Bull, 2008, 77(6):374-81.] - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rambousek L, Kleteckova L, Kubesova A, et al. Rat intrahippocampal NMDA infusion induces cell-specific damage and changes in expression of NMDA and GABA(A) receptor subunits. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0028390816300703. Neuropharmacology. 2016;105(13):594–606. [Rambousek L, Kleteckova L, Kubesova A, et al. Rat intrahippocampal NMDA infusion induces cell-specific damage and changes in expression of NMDA and GABA(A) receptor subunits[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2016, 105(13):594-606.] - PubMed
-
- Lee V, Mackenzie G, Hooper A, et al. Reduced tonic inhibition in the dentate gyrus contributes to chronic stress-induced impairments in learning and memory. Hippocampus. 2016;26(10):1276–90. doi: 10.1002/hipo.v26.10. [Lee V, Mackenzie G, Hooper A, et al. Reduced tonic inhibition in the dentate gyrus contributes to chronic stress-induced impairments in learning and memory[J]. Hippocampus, 2016, 26(10):1276-90.] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
