RSK2 contributes to myogenic vasoconstriction of resistance arteries by activating smooth muscle myosin and the Na+/H+ exchanger
- PMID: 30377223
- PMCID: PMC6474246
- DOI: 10.1126/scisignal.aar3924
RSK2 contributes to myogenic vasoconstriction of resistance arteries by activating smooth muscle myosin and the Na+/H+ exchanger
Abstract
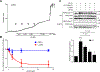
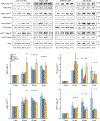
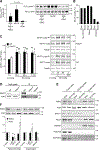
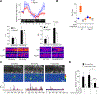
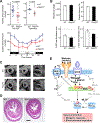
Smooth muscle contraction is triggered when Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) phosphorylates the regulatory light chain of myosin (RLC20). However, blood vessels from Mlck-deficient mouse embryos retain the ability to contract, suggesting the existence of additional regulatory mechanisms. We showed that the p90 ribosomal S6 kinase 2 (RSK2) also phosphorylated RLC20 to promote smooth muscle contractility. Active, phosphorylated RSK2 was present in mouse resistance arteries under normal basal tone, and phosphorylation of RSK2 increased with myogenic vasoconstriction or agonist stimulation. Resistance arteries from Rsk2-deficient mice were dilated and showed reduced myogenic tone and RLC20 phosphorylation. RSK2 phosphorylated Ser19 in RLC in vitro. In addition, RSK2 phosphorylated an activating site in the Na+/H+ exchanger (NHE-1), resulting in cytosolic alkalinization and an increase in intracellular Ca2+ that promotes vasoconstriction. NHE-1 activity increased upon myogenic constriction, and the increase in intracellular pH was suppressed in Rsk2-deficient mice. In pressured arteries, RSK2-dependent activation of NHE-1 was associated with increased intracellular Ca2+ transients, which would be expected to increase MLCK activity, thereby contributing to basal tone and myogenic responses. Accordingly, Rsk2-deficient mice had lower blood pressure than normal littermates. Thus, RSK2 mediates a procontractile signaling pathway that contributes to the regulation of basal vascular tone, myogenic vasoconstriction, and blood pressure and may be a potential therapeutic target in smooth muscle contractility disorders.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

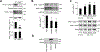
References
-
- Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV, Signal transduction and regulation in smooth muscle. Nature 372, 231–236 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV, Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: Modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol. Rev 83, 1325–1358 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Cole WC, Welsh DG, Role of myosin light chain kinase and myosin light chain phosphatase in the resistance arterial myogenic response to intravascular pressure. Arch. Biochem. Biophys 510, 160–173 (2011). - PubMed
-
- Somlyo AV, Wang H, Choudhury N, Khromov AS, Majesky M, Owens GK, Somlyo AP, Myosin light chain kinase knockout. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil 25, 241–242 (2004). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

