A light-gated potassium channel for sustained neuronal inhibition
- PMID: 30377377
- PMCID: PMC6834437
- DOI: 10.1038/s41592-018-0186-9
A light-gated potassium channel for sustained neuronal inhibition
Abstract
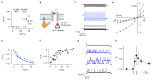
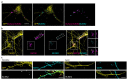
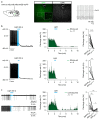
Currently available inhibitory optogenetic tools provide short and transient silencing of neurons, but they cannot provide long-lasting inhibition because of the requirement for high light intensities. Here we present an optimized blue-light-sensitive synthetic potassium channel, BLINK2, which showed good expression in neurons in three species. The channel is activated by illumination with low doses of blue light, and in our experiments it remained active over (tens of) minutes in the dark after the illumination was stopped. This activation caused long periods of inhibition of neuronal firing in ex vivo recordings of mouse neurons and impaired motor neuron response in zebrafish in vivo. As a proof-of-concept application, we demonstrated that in a freely moving rat model of neuropathic pain, the activation of a small number of BLINK2 channels caused a long-lasting (>30 min) reduction in pain sensation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests
Figures


Comment in
-
Anna Moroni.Nat Methods. 2018 Nov;15(11):841. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0192-y. Nat Methods. 2018. PMID: 30377370 No abstract available.
-
Two-component optogenetic inhibition.Nat Methods. 2019 Jan;16(1):26. doi: 10.1038/s41592-018-0285-7. Nat Methods. 2019. PMID: 30573828 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

