Resting heart rate and risk of type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30378246
- PMCID: PMC6398339
- DOI: 10.1002/dmrr.3095
Resting heart rate and risk of type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Positive association between resting heart rate (RHR) and risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) has been documented in several studies. However, whether RHR is an independent predictor of T2D and its potential interaction with other risk factors of T2D remain unclear.
Methods: We conducted a prospective cohort study of 31 156 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1992-2012). Cox proportional hazard model was used to examine the association between RHR and T2D risk. We further examined whether this association is modified by known risk factors. Lastly, we conducted a meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.
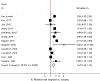
Results: During 505 380 person-years of follow-up, we identified 2338 incident T2D cases. The multivariable-adjusted hazard ratio (HR) comparing the highest vs lowest categories of RHR was 1.69 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.43-2.01). Increase in 10 bpm of RHR was associated with 19% increased risk of T2D in the fully adjusted model (HR, 1.19; 95% CI, 1.14-1.24). The HRs of T2D associated with RHR were stronger among those with normal weight or without hypertension (P interaction < 0.001). Moreover, RHR with other known risk factors cumulatively increased T2D risk. A meta-analysis consistently showed a positive association between RHR and T2D risk (the summary relative risk [RR] for highest vs lowest RHR, 1.53; 95% CI, 1.26-1.86, n = 12, the summary RR per 10 bpm increase, 1.17; 95% CI, 1.09-1.26, n = 13).
Conclusions: High RHR was independently associated with increased risk of T2D. Our findings suggest that RHR, with other known risk factors, could be a useful tool to predict T2D risk.
Keywords: interaction; meta-analysis; prospective cohort; resting heart rate; risk factor; type 2 diabetes.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of insulin resistance in the association between resting heart rate and type 2 diabetes: A prospective study.J Diabetes Complications. 2022 Nov;36(11):108319. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2022.108319. Epub 2022 Sep 27. J Diabetes Complications. 2022. PMID: 36279707
-
Resting heart rate and the risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus among non-diabetic and prediabetic Iranian adults: Tehran lipid and glucose study.BMC Public Health. 2023 Oct 27;23(1):2112. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-17022-7. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37891510 Free PMC article.
-
Association between resting heart rate and incident diabetes risk: a Mendelian randomization study.Acta Diabetol. 2019 Sep;56(9):1037-1044. doi: 10.1007/s00592-019-01344-3. Epub 2019 Apr 15. Acta Diabetol. 2019. PMID: 30989380
-
Resting heart rate and risk of incident heart failure: three prospective cohort studies and a systematic meta-analysis.J Am Heart Assoc. 2015 Jan 14;4(1):e001364. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.114.001364. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015. PMID: 25589535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Egg consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes: findings from 3 large US cohort studies of men and women and a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies.Am J Clin Nutr. 2020 Sep 1;112(3):619-630. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqaa115. Am J Clin Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32453379 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Increased resting heart rate and glucose metabolism in a community population.J Int Med Res. 2021 Nov;49(11):3000605211053754. doi: 10.1177/03000605211053754. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34814744 Free PMC article.
-
Association between resting heart rate and prognosis in patients with gastric cancer.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 24;15(1):6561. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89577-x. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39994270 Free PMC article.
-
Nocturnal heart rate during sleep is associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2531247. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2531247. Epub 2025 Jul 10. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 40638589 Free PMC article.
-
Heart Rate Variability and Incident Type 2 Diabetes in General Population.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023 Sep 18;108(10):2510-2516. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad200. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2023. PMID: 37022971 Free PMC article.
-
Resting heart rate is associated with the prevalence of chronic kidney disease in Korean adult: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Survey.BMC Public Health. 2024 Feb 5;24(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-17877-4. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38311734 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Organization WH. Global report on diabetes World Health Organization; 2016.
-
- Prevention. CfDCa. National Diabetes Statistics Report 2017.
-
- Aune D, Sen A, ó’Hartaigh B, et al. Resting heart rate and the risk of cardiovascular disease, total cancer, and all-cause mortality–A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2017. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

