Moderating effect of mode of delivery on the genetics of intelligence: Explorative genome-wide analyses in ALSPAC
- PMID: 30378284
- PMCID: PMC6305932
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1144
Moderating effect of mode of delivery on the genetics of intelligence: Explorative genome-wide analyses in ALSPAC
Abstract
Introduction: Intelligence is a core construct of individual differences in cognitive abilities and a strong predictor of important life outcomes. Within recent years, rates of cesarean section have substantially increased globally, though little is known about its effect on neurodevelopmental trajectories. Thus, we aimed to investigate the influence of delivery by cesarean section on the genetics of intelligence in children.
Methods: Participants were recruited through the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC). Intelligence was measured by the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC). Genotyping was performed using the Illumina Human Hap 550 quad genome-wide SNP genotyping platform and was followed by imputation using MACH software. Genome-wide interaction analyses were conducted using linear regression.
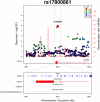
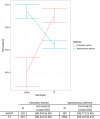
Results: A total of 2,421 children and 2,141,747 SNPs were subjected to the genome-wide interaction analyses. No variant reached genome-wide significance. The strongest interaction was observed at rs17800861 in the GRIN2A gene (β = -3.43, 95% CI = -4.74 to -2.12, p = 2.98E-07). This variant is predicted to be located within active chromatin compartments in the hippocampus and may influence binding of the NF-kappaB transcription factor.
Conclusions: Our results may indicate that mode of delivery might have a moderating effect on genetic disposition of intelligence in children. Studies of considerable sizes (>10,000) are likely required to more robustly detect variants governing such interaction. In summary, the presented findings prompt the need for further studies aimed at increasing our understanding of effects various modes of delivery may have on health outcomes in children.
Keywords: Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children; glutamate; intelligence; mode of delivery.
© 2018 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implication of the APP Gene in Intellectual Abilities.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;59(2):723-735. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170049. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 28671113 Free PMC article.
-
Childhood intelligence is heritable, highly polygenic and associated with FNBP1L.Mol Psychiatry. 2014 Feb;19(2):253-8. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.184. Epub 2013 Jan 29. Mol Psychiatry. 2014. PMID: 23358156 Free PMC article.
-
The developmental genetic architecture of vocabulary skills during the first three years of life: Capturing emerging associations with later-life reading and cognition.PLoS Genet. 2021 Feb 12;17(2):e1009144. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1009144. eCollection 2021 Feb. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 33577555 Free PMC article.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
The new genetics of intelligence.Nat Rev Genet. 2018 Mar;19(3):148-159. doi: 10.1038/nrg.2017.104. Epub 2018 Jan 8. Nat Rev Genet. 2018. PMID: 29335645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Children's Greenness Exposure and IQ-Associated DNA Methylation: A Prospective Cohort Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Jul 12;18(14):7429. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18147429. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34299878 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the interplay of Caesarean delivery and genetic influences on intelligence and anxiety traits in offspring findings from genome-wide association studies.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2025 Mar 5;25:100377. doi: 10.1016/j.eurox.2025.100377. eCollection 2025 Mar. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol X. 2025. PMID: 40125487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Are there adverse outcomes for child health and development following caesarean section delivery? Can we justify using elective caesarean section to prevent obstetric pelvic floor damage?Int Urogynecol J. 2021 Jul;32(7):1963-1969. doi: 10.1007/s00192-021-04781-3. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Int Urogynecol J. 2021. PMID: 33877375 Review.
-
Influence of Mode of Delivery on Children's Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder and Childhood Intelligence.Psychiatry Investig. 2023 Aug;20(8):714-720. doi: 10.30773/pi.2022.0310. Epub 2023 Aug 11. Psychiatry Investig. 2023. PMID: 37559451 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bassett, A. S. , Chow, E. W. C. , Waterworth, D. M. , & Linda, B.(2008). Genetic insights into Schizophrenia. Disability and Rehabilitation, 49(2), 743–750. 10.1167/iovs.07-1072 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

