Worry is associated with inefficient functional activity and connectivity in prefrontal and cingulate cortices during emotional interference
- PMID: 30378289
- PMCID: PMC6305912
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.1137
Worry is associated with inefficient functional activity and connectivity in prefrontal and cingulate cortices during emotional interference
Abstract
Introduction: Anxiety is known to impair attentional control particularly when Task demands are high. Neuroimaging studies generally support these behavioral findings, reporting that anxiety is associated with increased (inefficient) activity in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) and anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) during attentional control Tasks. However, less is known about the relationship between worry (part of the cognitive dimension of trait anxiety) and DLPFC/ACC function and connectivity during attentional control. In the present study, we sought to clarify this relationship.
Methods: Forty-one participants underwent functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) during a composite Faces and Scenes Task with high and low emotional interference conditions. Individual worry levels were assessed using the Penn State Worry Questionnaire.
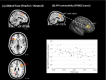
Results: During high but not low emotional interference, worry was associated with increased activity in ACC, DLPFC, insula, and inferior parietal cortex. During high emotional interference, worry was also associated with reduced functional connectivity between ACC and DLPFC. Trait anxiety was not associated with changes in DLPFC/ACC activity or connectivity during either Task condition.
Conclusions: The results are consistent with cognitive models that propose worry competes for limited processing resources resulting in inefficient DLPFC and ACC activity when Tasks demands are high. Limitations of the present study and directions for future work are discussed.
Keywords: anterior cingulate; anxiety; dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; functional magnetic resonance imaging; worry.
© 2018 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Using connectivity-based real-time fMRI neurofeedback to modulate attentional and resting state networks in people with high trait anxiety.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;25:102191. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102191. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 32044712 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the anxious mind: anxiety, worry, and frontal engagement in sustained attention versus off-task processing.Cereb Cortex. 2015 Mar;25(3):609-18. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bht248. Epub 2013 Sep 22. Cereb Cortex. 2015. PMID: 24062316 Free PMC article.
-
Trait anxiety modulates anterior cingulate activation to threat interference.Depress Anxiety. 2011 Mar;28(3):194-201. doi: 10.1002/da.20802. Depress Anxiety. 2011. PMID: 21394852 Free PMC article.
-
Functional imaging of brain responses to pain. A review and meta-analysis (2000).Neurophysiol Clin. 2000 Oct;30(5):263-88. doi: 10.1016/s0987-7053(00)00227-6. Neurophysiol Clin. 2000. PMID: 11126640 Review.
-
Altered Task-Evoked Corticolimbic Responsivity in Generalized Anxiety Disorder.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 31;22(7):3630. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073630. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33807276 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The unique face of anxious depression: Increased sustained threat circuitry response during fear acquisition.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Oct 17:2023.10.17.562565. doi: 10.1101/2023.10.17.562565. bioRxiv. 2023. PMID: 37905149 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Trait Anxiety, Emotion Regulation, and Metacognitive Beliefs: An Observational Study Incorporating Separate Network and Correlation Analyses to Examine Associations with Executive Functions and Academic Achievement.Children (Basel). 2024 Jan 18;11(1):123. doi: 10.3390/children11010123. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38255435 Free PMC article.
-
Regional Brain Gray Matter Changes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Sci Rep. 2020 Jun 18;10(1):9925. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-67022-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32555374 Free PMC article.
-
Functional brain abnormalities associated with comorbid anxiety in autism spectrum disorder.Dev Psychopathol. 2020 Oct;32(4):1273-1286. doi: 10.1017/S0954579420000772. Dev Psychopathol. 2020. PMID: 33161905 Free PMC article.
-
Task-based attentional and default mode connectivity associated with science and math anxiety profiles among university physics students.Trends Neurosci Educ. 2023 Sep;32:100204. doi: 10.1016/j.tine.2023.100204. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Trends Neurosci Educ. 2023. PMID: 37689430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barlow, D. H. (1991). Disorders of emotion. Psychological Inquiry, 2, 58–71. 10.1207/s15327965pli0201_15 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

