Goal-directed therapy in patients with early acute kidney injury: a multicenter randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 30379222
- PMCID: PMC6201149
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2018/e327
Goal-directed therapy in patients with early acute kidney injury: a multicenter randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Objectives: Acute kidney injury is associated with many conditions, and no interventions to improve the outcomes of established acute kidney injury have been developed. We performed this study to determine whether goal-directed therapy conducted during the early stages of acute kidney injury could change the course of the disease.
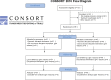
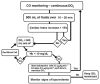
Methods: This was a multicenter prospective randomized controlled study. Patients with early acute kidney injury in the critical care unit were randomly allocated to a standard care (control) group or a goal-directed therapy group with 8h of intensive treatment to maximize oxygen delivery, and all patients were evaluated during a period of 72h. ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02414906.
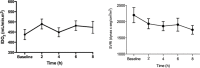
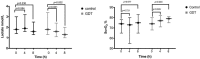
Results: A total of 143 patients were eligible for the study, and 99 patients were randomized. Central venous oxygen saturation was significantly increased and the serum lactate level significantly was decreased from baseline levels in the goal-directed therapy group (p=0.001) compared to the control group (p=0.572). No significant differences in the change in serum creatinine level (p=0.96), persistence of acute kidney injury beyond 72h (p=0.064) or the need for renal replacement therapy (p=0.82) were observed between the two groups. In-hospital mortality was significantly lower in the goal-directed therapy group than in the control group (33% vs. 51%; RR: 0.61, 95% CI: 0.37-1.00, p=0.048, number needed to treat=5).
Conclusions: Goal-directed therapy for patients in the early stages of acute kidney injury did not change the disease course.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

