Simultaneous induction of dispersed and clustered DNA lesions compromises DNA damage response in human peripheral blood lymphocytes
- PMID: 30379881
- PMCID: PMC6209146
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0204068
Simultaneous induction of dispersed and clustered DNA lesions compromises DNA damage response in human peripheral blood lymphocytes
Abstract
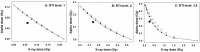
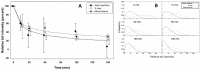
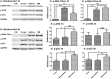
Due to its ability to induce DNA damage in a space and time controlled manner, ionising radiation is a unique tool for studying the mechanisms of DNA repair. The biological effectiveness of ionising radiation is related to the ionisation density which is defined by the linear energy transfer (LET). Alpha particles are characterised by high LET, while X-rays by low LET values. An interesting question is how cells react when exposed to a mixed beam of high and low LET radiation. In an earlier study carried out with human peripheral blood lymphocytes (PBL) we could demonstrate that alpha radiation X-rays interact in producing more chromosomal aberrations than expected based on additivity. The aim of the present investigation was to look at the mechanism of the interaction, especially with respect to the question if it is due to an augmented level of initial damage or impaired DNA repair. PBL were exposed to various doses of alpha particles, X-rays and mixed beams. DNA damage and the kinetics of damage repair was quantified by the alkaline comet assay. The levels of phosphorylated, key DNA damage response (DDR) proteins ATM, p53 and DNA-PK were measured by Western blotting and mRNA levels of 6 damage-responsive genes were measured by qPCR. Alpha particles and X-rays interact in inducing DNA damage above the level predicted by assuming additivity and that the repair of damage occurs with a delay. The activation levels of DDR proteins and mRNA levels of the studied genes were highest in cells exposed to mixed beams. The results substantiate the idea that exposure to mixed beams presents a challenge for the cellular DDR system.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Complex aberrations in lymphocytes exposed to mixed beams of (241)Am alpha particles and X-rays.Mutat Res. 2013 Aug 30;756(1-2):95-100. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 May 10. Mutat Res. 2013. PMID: 23669292
-
Chromosomal damage, gene expression and alternative transcription in human lymphocytes exposed to mixed ionizing radiation as encountered in space.Sci Rep. 2024 May 20;14(1):11502. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62313-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38769353 Free PMC article.
-
Investigation of switch from ATM to ATR signaling at the sites of DNA damage induced by low and high LET radiation.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Dec;12(12):1143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Nov 12. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 24238855
-
The Cellular Response to Complex DNA Damage Induced by Ionising Radiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 3;24(5):4920. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054920. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902352 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of DNA-PK and ATM in radiation- and heat-induced DNA damage recognition and apoptotic cell death.J Radiat Res. 2010;51(5):493-501. doi: 10.1269/jrr.10039. Epub 2010 Aug 28. J Radiat Res. 2010. PMID: 20814172 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer Studies under Space Conditions: Finding Answers Abroad.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 23;10(1):25. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010025. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 35052703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Validation of a High-Throughput Dicentric Chromosome Assay Using Complex Radiation Exposures.Radiat Res. 2023 Jan 1;199(1):1-16. doi: 10.1667/RADE-22-00007.1. Radiat Res. 2023. PMID: 35994701 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Effects of UVB and Ionizing Radiation on Human Non-Malignant Cells: Implications for Ozone Depletion and Secondary Cosmic Radiation Exposure.Biomolecules. 2025 Apr 6;15(4):536. doi: 10.3390/biom15040536. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40305266 Free PMC article.
-
Suppressed DNA repair capacity in flight attendants after air travel.Sci Rep. 2025 May 13;15(1):16513. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98934-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40360675 Free PMC article.
-
Ionizing Radiation and Complex DNA Damage: From Prediction to Detection Challenges and Biological Significance.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Nov 14;11(11):1789. doi: 10.3390/cancers11111789. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31739493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Schrödinger E. What is life? Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 1946.
-
- Jeggo PA. DNA breakage and repair. Advances in Genetics 1998;38:185219. - PubMed
-
- Kerzendorfer C, O’Driscoll M. Human DNA damage response and repair deficiency syndromes: linking genomic instability and cell cycle checkpoint proficiency. DNA Repair (Amst) 2009. September 2;8(9):1139–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

