Axon numbers and landmarks of trigeminal donor nerves for corneal neurotization
- PMID: 30379941
- PMCID: PMC6209308
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206642
Axon numbers and landmarks of trigeminal donor nerves for corneal neurotization
Erratum in
-
Correction: Axon numbers and landmarks of trigeminal donor nerves for corneal neurotization.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 28;14(2):e0211748. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211748. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30817768 Free PMC article.
Abstract
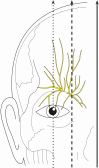
Purpose: Corneal anesthesia leads to chronic corneal injury. This anatomical study characterizes the donor nerve branches of the supratrochlear and supraorbital nerves used for corneal neurotization.
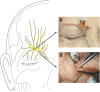
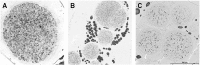
Methods: In 13 non-embalmed cadavers, the supratrochlear and supraorbital nerves were dissected and distances to anatomical landmarks measured. Cross-sections of supratrochlear and supraorbital donor nerves were harvested and histomorphometrically analyzed to assess the number of myelinated axons.
Results: The donor axon counts were 3146 ± 1069.9 for the supratrochlear and 1882 ± 903 for the supraorbital nerve distal to the supraorbital notch. The supratrochlear nerve was dissected on the medial upper eyelid 2 cm lateral to the facial midline and the branch of the supraorbital nerve 1 cm medial to the mid-pupillary line.
Conclusion: The supraorbital and supratrochlear branches of the trigeminal nerve are potent donor nerves for corneal neurotization in the treatment of neuropathic keratopathy and can be reliably dissected using anatomical landmarks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Muller LJ, Marfurt CF, Kruse F, Tervo TM. Corneal nerves: structure, contents and function. Exp Eye Res. 2003;76(5):521–42. Epub 2003/04/17. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

