CD47 Blockade by Hu5F9-G4 and Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
- PMID: 30380386
- PMCID: PMC8058634
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1807315
CD47 Blockade by Hu5F9-G4 and Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Abstract
Background: The Hu5F9-G4 (hereafter, 5F9) antibody is a macrophage immune checkpoint inhibitor blocking CD47 that induces tumor-cell phagocytosis. 5F9 synergizes with rituximab to eliminate B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma cells by enhancing macrophage-mediated antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis. This combination was evaluated clinically.
Methods: We conducted a phase 1b study involving patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Patients may have had diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or follicular lymphoma. 5F9 (at a priming dose of 1 mg per kilogram of body weight, administered intravenously, with weekly maintenance doses of 10 to 30 mg per kilogram) was given with rituximab to determine safety and efficacy and to suggest a phase 2 dose.
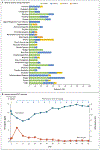
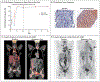
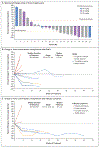
Results: A total of 22 patients (15 with DLBCL and 7 with follicular lymphoma) were enrolled. Patients had received a median of 4 (range, 2 to 10) previous therapies, and 95% of the patients had disease that was refractory to rituximab. Adverse events were predominantly of grade 1 or 2. The most common adverse events were anemia and infusion-related reactions. Anemia (an expected on-target effect) was mitigated by the strategy of 5F9 prime and maintenance dosing. Dose-limiting side effects were rare. A selected phase 2 dose of 30 mg of 5F9 per kilogram led to an approximate 100% CD47-receptor occupancy on circulating white and red cells. A total of 50% of the patients had an objective (i.e., complete or partial) response, with 36% having a complete response. The rates of objective response and complete response were 40% and 33%, respectively, among patients with DLBCL and 71% and 43%, respectively, among those with follicular lymphoma. At a median follow-up of 6.2 months among patients with DLBCL and 8.1 months among those with follicular lymphoma, 91% of the responses were ongoing.
Conclusions: The macrophage checkpoint inhibitor 5F9 combined with rituximab showed promising activity in patients with aggressive and indolent lymphoma. No clinically significant safety events were observed in this initial study. (Funded by Forty Seven and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02953509 .).
Figures
Comment in
-
Macrophage Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer - Back to the Future.N Engl J Med. 2018 Nov 1;379(18):1777-1779. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1811699. N Engl J Med. 2018. PMID: 30380398 No abstract available.
-
Anti-CD47 Agent Boosts Macrophage Activity in NHL.Cancer Discov. 2019 Jan;9(1):7-8. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2018-155. Epub 2018 Nov 21. Cancer Discov. 2019. PMID: 30464001
-
Myeloid immune-checkpoint inhibition enters the clinical stage.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019 May;16(5):275-276. doi: 10.1038/s41571-018-0155-3. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30573788 No abstract available.
-
CD47 Blockade and Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 31;380(5):496-7. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1816156. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 30702240 No abstract available.
-
CD47 Blockade and Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma.N Engl J Med. 2019 Jan 31;380(5):497. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1816156. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 30702241 No abstract available.
References
-
- Keating GM. Rituximab: a review of its use in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia, low-grade or follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Drugs 2010;70:1445–76. - PubMed
-
- Solal-Céligny P, Leconte P, Bardet A, Hernandez J, Troussard X. A retrospective study on the management of patients with rituximab refractory follicular lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2018;180:217–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
