New genetic players in late-onset Alzheimer's disease: Findings of genome-wide association studies
- PMID: 30381536
- PMCID: PMC6206761
- DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_473_17
New genetic players in late-onset Alzheimer's disease: Findings of genome-wide association studies
Abstract
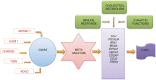
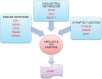
Late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD) or sporadic AD is the most common form of AD. The precise pathogenetic changes that trigger the development of AD remain largely unknown. Large-scale genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have identified single-nucleotide polymorphisms in multiple genes which are associated with AD; most notably, these are ABCA7, bridging integrator 1 (B1N1), triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2), CD33, clusterin (CLU), complement receptor 1 (CRI), ephrin type-A receptor 1 (EPHA1), membrane-spanning 4-domains, subfamily A (MS4A) and phosphatidylinositol binding clathrin assembly protein (PICALM) genes. The proteins coded by the candidate genes participate in a variety of cellular processes such as oxidative balance, protein metabolism, cholesterol metabolism and synaptic function. This review summarizes the major gene loci affecting LOAD identified by large GWASs. Tentative mechanisms have also been elaborated in various studies by which the proteins coded by these genes may exert a role in AD pathogenesis have also been elaborated. The review suggests that these may together affect LOAD pathogenesis in a complementary fashion.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology; LOAD; Translational Genomics Research Institute; genome-wide association study; single nucleotide polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
References
-
- Tiraboschi P, Hansen LA, Thal LJ, Corey-Bloom J. The importance of neuritic plaques and tangles to the development and evolution of AD. Neurology. 2004;62:1984–9. - PubMed
-
- Ward A, Crean S, Mercaldi CJ, Collins JM, Boyd D, Cook MN, et al. Prevalence of apolipoprotein E4 genotype and homozygotes (APOE e4/4) among patients diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology. 2012;38:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Nathan BP, Bellosta S, Sanan DA, Weisgraber KH, Mahley RW, Pitas RE, et al. Differential effects of apolipoproteins E3 and E4 on neuronal growth in vitro . Science. 1994;264:850–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
