YAP1 enhances NF-κB-dependent and independent effects on clock-mediated unfolded protein responses and autophagy in sarcoma
- PMID: 30382078
- PMCID: PMC6208433
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-018-1142-4
YAP1 enhances NF-κB-dependent and independent effects on clock-mediated unfolded protein responses and autophagy in sarcoma
Abstract
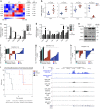
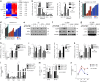
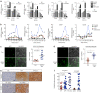
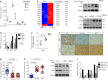
Terminal differentiation opposes proliferation in the vast majority of tissue types. As a result, loss of lineage differentiation is a hallmark of aggressive cancers, including soft tissue sarcomas (STS). Consistent with these observations, undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (UPS), an STS subtype devoid of lineage markers, is among the most lethal sarcomas in adults. Though tissue-specific features are lost in these mesenchymal tumors they are most commonly diagnosed in skeletal muscle, and are thought to develop from transformed muscle progenitor cells. We have found that a combination of HDAC (Vorinostat) and BET bromodomain (JQ1) inhibition partially restores differentiation to skeletal muscle UPS cells and tissues, enforcing a myoblast-like identity. Importantly, differentiation is partially contingent upon downregulation of the Hippo pathway transcriptional effector Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) and nuclear factor (NF)-κB. Previously, we observed that Vorinostat/JQ1 inactivates YAP1 and restores oscillation of NF-κB in differentiating myoblasts. These effects correlate with reduced tumorigenesis, and enhanced differentiation. However, the mechanisms by which the Hippo/NF-κB axis impact differentiation remained unknown. Here, we report that YAP1 and NF-κB activity suppress circadian clock function, inhibiting differentiation and promoting proliferation. In most tissues, clock activation is antagonized by the unfolded protein response (UPR). However, skeletal muscle differentiation requires both Clock and UPR activity, suggesting the molecular link between them is unique in muscle. In skeletal muscle-derived UPS, we observed that YAP1 suppresses PERK and ATF6-mediated UPR target expression as well as clock genes. These pathways govern metabolic processes, including autophagy, and their disruption shifts metabolism toward cancer cell-associated glycolysis and hyper-proliferation. Treatment with Vorinostat/JQ1 inhibited glycolysis/MTOR signaling, activated the clock, and upregulated the UPR and autophagy via inhibition of YAP1/NF-κB. These findings support the use of epigenetic modulators to treat human UPS. In addition, we identify specific autophagy, UPR, and muscle differentiation-associated genes as potential biomarkers of treatment efficacy and differentiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
YAP1-Mediated Suppression of USP31 Enhances NFκB Activity to Promote Sarcomagenesis.Cancer Res. 2018 May 15;78(10):2705-2720. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-4052. Epub 2018 Feb 28. Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29490948 Free PMC article.
-
A PERK-miR-211 axis suppresses circadian regulators and protein synthesis to promote cancer cell survival.Nat Cell Biol. 2018 Jan;20(1):104-115. doi: 10.1038/s41556-017-0006-y. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Nat Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29230015 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Hippo coactivator YAP1 through BET bromodomain inhibition in esophageal adenocarcinoma.Mol Oncol. 2020 Jun;14(6):1410-1426. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12667. Epub 2020 Apr 7. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32175692 Free PMC article.
-
The Hippo signal transduction pathway in soft tissue sarcomas.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Aug;1856(1):121-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2015.05.006. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26050962 Review.
-
Circadian Clock, Glucocorticoids and NF-κB Signaling in Neuroinflammation- Implicating Glucocorticoid Induced Leucine Zipper as a Molecular Link.ASN Neuro. 2022 Jan-Dec;14:17590914221120190. doi: 10.1177/17590914221120190. ASN Neuro. 2022. PMID: 36317290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Insights Into Cancer Chronotherapies.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 13;12:741295. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.741295. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34966277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDAC-an important target for improving tumor radiotherapy resistance.Front Oncol. 2023 Jul 12;13:1193637. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1193637. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37503317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
H3K27ac-activated LINC00519 promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting miR-450b-5p/miR-515-5p/YAP1 axis.Cell Prolif. 2020 May;53(5):e12797. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12797. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Cell Prolif. 2020. PMID: 32297697 Free PMC article.
-
SON-dependent nuclear speckle rehabilitation alleviates proteinopathies.Nat Commun. 2025 Aug 5;16(1):7065. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62242-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40764481 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Expression of YAP Inhibited the Autophagy Level by Upregulating mTOR Signal in the Eutopic ESCs of Endometriosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jan 31;13:813165. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.813165. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35173685 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pappo AS, et al. A phase 2 trial of R1507, a monoclonal antibody to the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R), in patients with recurrent or refractory rhabdomyosarcoma, osteosarcoma, synovial sarcoma, and other soft tissue sarcomas: results of a Sarcoma Alliance for Research Through Collaboration study. Cancer. 2014;120:2448–2456. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28728. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

