Stress rapidly suppresses in vivo LH pulses and increases activation of RFRP-3 neurons in male mice
- PMID: 30382693
- PMCID: PMC6214202
- DOI: 10.1530/JOE-18-0449
Stress rapidly suppresses in vivo LH pulses and increases activation of RFRP-3 neurons in male mice
Abstract
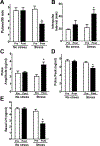
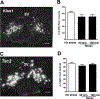
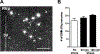
Restraint stress is a psychosocial stressor that suppresses reproductive status, including LH pulsatile secretion, but the neuroendocrine mechanisms underlying this inhibition remains unclear. Reproductive neural populations upstream of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons, such as kisspeptin, neurokinin B and RFRP-3 (GnIH) neurons, are possible targets for psychosocial stress to inhibit LH pulses, but this has not been well examined, especially in mice in which prior technical limitations prevented assessment of in vivo LH pulse secretion dynamics. Here, we examined whether one-time acute restraint stress alters in vivo LH pulsatility and reproductive neural populations in male mice, and what the time-course is for such alterations. We found that endogenous LH pulses in castrated male mice are robustly and rapidly suppressed by one-time, acute restraint stress, with suppression observed as quickly as 12–18 min. This rapid LH suppression parallels with increased in vivo corticosterone levels within 15 min of restraint stress. Although Kiss1, Tac2 and Rfrp gene expression in the hypothalamus did not significantly change after 90 or 180 min restraint stress, arcuate Kiss1 neural activation was significantly decreased after 180 min. Interestingly, hypothalamic Rfrp neuronal activation was strongly increased at early times after restraint stress initiation, but was attenuated to levels lower than controls by 180 min of restraint stress. Thus, the male neuroendocrine reproductive axis is quite sensitive to short-term stress exposure, with significantly decreased pulsatile LH secretion and increased hypothalamic Rfrp neuronal activation occurring rapidly, within minutes, and decreased Kiss1 neuronal activation also occurring after longer stress durations.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

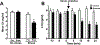



References
-
- Anderson GM, Relf HL, Rizwan MZ & Evans JJ 2009. Central and peripheral effects of RFamide-related peptide-3 on luteinizing hormone and prolactin secretion in rats. Endocrinology 150 1834–1840. - PubMed
-
- Chen MD, O’Byrne KT, Chiappini SE, Hotchkiss J & Knobil E 1992. Hypoglycemic ‘stress’ and gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse generator activity in the rhesus monkey: role of the ovary. Neuroendocrinology 56 666–673. - PubMed
-
- Chen MD, Ordog T, O’Byrne KT, Goldsmith JR, Connaughton MA & Knobil E 1996. The insulin hypoglycemia-induced inhibition of gonadotropin-releasing hormone pulse generator activity in the rhesus monkey: roles of vasopressin and corticotropin-releasing factor. Endocrinology 137 2012–2021. - PubMed
-
- Clarke IJ, Sari IP, Qi Y, Smith JT, Parkington HC, Ubuka T, Iqbal J, Li Q, Tilbrook A, Morgan K, et al. 2008. Potent action of RFamide-related peptide-3 on pituitary gonadotropes indicative of a hypophysiotropic role in the negative regulation of gonadotropin secretion. Endocrinology 149 5811–5821. - PubMed

