Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 3 novel loci associated with stroke
- PMID: 30383316
- PMCID: PMC6644297
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.25369
Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 3 novel loci associated with stroke
Abstract
We conducted a European-only and transancestral genome-wide association meta-analysis in 72,147 stroke patients and 823,869 controls using data from UK Biobank (UKB) and the MEGASTROKE consortium. We identified an exonic polymorphism in NOS3 (rs1799983, p.Glu298Asp; p = 2.2E-8, odds ratio [OR] = 1.05, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.04-1.07) and variants in an intron of COL4A1 (rs9521634; p = 3.8E-8, OR = 1.04, 95% CI = 1.03-1.06) and near DYRK1A (rs720470; p = 6.1E-9, OR = 1.05, 95% CI = 1.03-1.07) at genome-wide significance for stroke. Effect sizes of known stroke loci were highly correlated between UKB and MEGASTROKE. Using Mendelian randomization, we further show that genetic variation in the nitric oxide synthase-nitric oxide pathway in part affects stroke risk via variation in blood pressure. Ann Neurol 2018;84:934-939.
© 2018 The Authors. Annals of Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to report.
Figures

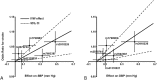
References
-
- Woodfield R, Grant I, UK Biobank Stroke Outcomes Group, UK Biobank Follow‐up Outcomes Working Group , Sudlow CL. Accuracy of electronic health record data for identifying stroke cases in large‐scale epidemiological studies: a systematic review from the UK Biobank Stroke Outcomes Group. PLoS One 2015;10:e0140533. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

