Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction for hyperlipidemia: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30383686
- PMCID: PMC6221624
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013067
Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction for hyperlipidemia: Protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Hyperlipidemia is one of the most common metabolic diseases worldwide, as well as a leading risk factor for cardio-cerebrovascular diseases. Banxia Baizhu Tianma decoction (BBTD) is widely used for the treatment of hyperlipidemia in China, however, systematic review and meta-analysis regarding its efficacy and safety is lacking. The aim of this protocol of systematic review is to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of BBTD in the treatment of hyperlipidemia.
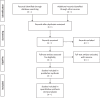
Methods: We will include the randomized controlled trials estimating the effectiveness and safety of BBTD in the treatment of hyperlipidemia. Data sources will include 5 English databases (PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, CINAHL) and 4 Chinese databases (CMB, CNKI, VIP, Wanfang database). The literature to be collected will be from the time when databases were established to September 2018. Efficacy will be accepted as the primary outcome, while blood lipid levels and adverse reactions as the secondary outcome. Study selection, data collection, risk of bias assessment, and evaluation of the quality of the evidence will be conducted by 2 × 2 different reviewers. Statistical syntheses will be conducted by using RevMan software V.5.3.
Results: This study will provide a high-quality evidence for BBTD on the treatment of hyperlipidemia from efficacy, serum lipid levels, and adverse reactions.
Conclusion: The result will provide a basis for judging whether BBTD is an effective intervention for the treatment of hyperlipidemia.
Prospero registration number: PROSPERO CRD 42018081359.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
References
-
- Jacobson TA, Ito MK, Maki KC, et al. National Lipid Association recommendations for patient-centered management of dyslipidemia: part 1 - executive summary. J Clin Lipidol 2015;9:129–69. - PubMed
-
- Rader DJ. Effect of insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and intra-abdominal adiposity on the development of cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus. Am J Med 2007;120:S12–8. - PubMed
-
- Jellinger PS, Smith DA, Mehta AE, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists’ guidelines for management of dyslipidemia and prevention of atherosclerosis. Endocrine Pract 2012;18:269–93. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources