Comparison of the Diagnostic Accuracies of 1.5T and 3T Stress Myocardial Perfusion Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance for Detecting Significant Coronary Artery Disease
- PMID: 30386133
- PMCID: PMC6201977
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.6.1007
Comparison of the Diagnostic Accuracies of 1.5T and 3T Stress Myocardial Perfusion Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance for Detecting Significant Coronary Artery Disease
Abstract
Objective: To compare the diagnostic performance of cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) myocardial perfusion at 1.5- and 3-tesla (T) for detecting significant coronary artery disease (CAD), with invasive coronary angiography (ICA) as the reference method.
Materials and methods: We prospectively enrolled 281 patients (age 62.4 ± 8.3 years, 193 men) with suspected or known CAD who had undergone 1.5T or 3T CMR and ICA. Two independent radiologists interpreted perfusion defects. With ICA as the reference standard, the diagnostic performance of 1.5T and 3T CMR for identifying significant CAD (≥ 50% diameter reduction of the left main and ≥ 70% diameter reduction of other epicardial arteries) was determined.
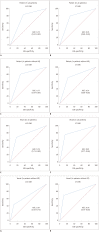
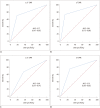
Results: No differences were observed in baseline characteristics or prevalence of CAD and old myocardial infarction (MI) using 1.5T (n = 135) or 3T (n = 146) systems. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values, and area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for detecting significant CAD were similar between the 1.5T (84%, 64%, 74%, 76%, and 0.75 per patient and 68%, 83%, 66%, 84%, and 0.76 per vessel) and 3T (80%, 71%, 71%, 80%, and 0.76 per patient and 75%, 86%, 64%, 91%, and 0.81 per vessel) systems. In patients with multi-vessel CAD without old MI, the sensitivity, specificity, and AUC with 3T were greater than those with 1.5T on a per-vessel basis (71% vs. 36%, 92% vs. 69%, and 0.82 vs. 0.53, respectively).
Conclusion: 3T CMR has similar diagnostic performance to 1.5T CMR in detecting significant CAD, except for higher diagnostic performance in patients with multi-vessel CAD without old MI.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Coronary artery disease; Invasive coronary angiography, 3 tesla; Magnetic resonance imaging; Myocardial perfusion.
Figures



References
-
- Takx RA, Blomberg BA, El Aidi H, Habets J, de Jong PA, Nagel E, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of stress myocardial perfusion imaging compared to invasive coronary angiography with fractional flow reserve meta-analysis. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;8:pii: e002666 - PubMed
-
- Rieber J, Huber A, Erhard I, Mueller S, Schweyer M, Koenig A, et al. Cardiac magnetic resonance perfusion imaging for the functional assessment of coronary artery disease: a comparison with coronary angiography and fractional flow reserve. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:1465–1471. - PubMed
-
- Groothuis JG, Beek AM, Brinckman SL, Meijerink MR, van den Oever ML, Hofman MB, et al. Combined non-invasive functional and anatomical diagnostic work-up in clinical practice: the magnetic resonance and computed tomography in suspected coronary artery disease (MARCC) study. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:1990–1998. - PubMed
-
- Rajiah P, Bolen MA. Cardiovascular MR imaging at 3 T: opportunities, challenges, and solutions. Radiographics. 2014;34:1612–1635. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

