Genome editing of oncogenes with ZFNs and TALENs: caveats in nuclease design
- PMID: 30386178
- PMCID: PMC6198504
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-018-0666-0
Genome editing of oncogenes with ZFNs and TALENs: caveats in nuclease design
Abstract
Background: Gene knockout technologies involving programmable nucleases have been used to create knockouts in several applications. Gene editing using Zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs), Transcription activator like effectors (TALEs) and CRISPR/Cas systems has been used to create changes in the genome in order to make it non-functional. In the present study, we have looked into the possibility of using six fingered CompoZr ZFN pair to target the E6 gene of HPV 16 genome.
Methods: HPV 16+ve cell lines; SiHa and CaSki were used for experiments. CompoZr ZFNs targeting E6 gene were designed and constructed by Sigma-Aldrich. TALENs targeting E6 and E7 genes were made using TALEN assembly kit. Gene editing was monitored by T7E1 mismatch nuclease and Nuclease resistance assays. Levels of E6 and E7 were further analyzed by RT-PCR, western blot as well as immunoflourescence analyses. To check if there is any interference due to methylation, cell lines were treated with sodium butyrate, and Nocodazole.
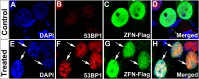
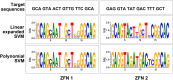
Results: Although ZFN editing activity in yeast based MEL-I assay was high, it yielded very low activity in tumor cell lines; only 6% editing in CaSki and negligible activity in SiHa cell lines. Though editing efficiency was better in CaSki, no significant reduction in E6 protein levels was observed in immunocytochemical analysis. Further, in silico analysis of DNA binding prediction revealed that some of the ZFN modules bound to sequence that did not match the target sequence. Hence, alternate ZFN pairs for E6 and E7 were not synthesized since no further active sites could be identified by in silico analyses. Then we designed TALENs to target E6 and E7 gene. TALENs designed to target E7 gene led to reduction of E7 levels in CaSki and SiHa cervical cancer cell lines. However, TALEN designed to target E6 gene did not yield any editing activity.
Conclusions: Our study highlights that designed nucleases intended to obtain bulk effect should have a reasonable editing activity which reflects phenotypically as well. Nucleases with low editing efficiency, intended for generation of knockout cell lines nucleases could be obtained by single cell cloning. This could serve as a criterion for designing ZFNs and TALENs.
Keywords: Cervical cancer; Gene editing; HPV; TALEN; Zinc-finger nucleases.
Figures





Similar articles
-
The comparison of ZFNs, TALENs, and SpCas9 by GUIDE-seq in HPV-targeted gene therapy.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Aug 19;26:1466-1478. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.08.008. eCollection 2021 Dec 3. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 34938601 Free PMC article.
-
TALEN based HPV-E7 editing triggers necrotic cell death in cervical cancer cells.Sci Rep. 2017 Jul 14;7(1):5500. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-05696-0. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28710417 Free PMC article.
-
Genome editing with CompoZr custom zinc finger nucleases (ZFNs).J Vis Exp. 2012 Jun 14;(64):e3304. doi: 10.3791/3304. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22732945 Free PMC article.
-
TALENs-an indispensable tool in the era of CRISPR: a mini review.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021 Aug 21;19(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s43141-021-00225-z. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34420096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origins of Programmable Nucleases for Genome Engineering.J Mol Biol. 2016 Feb 27;428(5 Pt B):963-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2015.10.014. Epub 2015 Oct 23. J Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26506267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome editing via non-viral delivery platforms: current progress in personalized cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2022 Mar 11;21(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01550-8. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35277177 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Advances in Genome-Editing Technology with CRISPR/Cas9 Variants and Stimuli-Responsive Targeting Approaches within Tumor Cells: A Future Perspective of Cancer Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 11;24(8):7052. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087052. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108214 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Designer nucleases to treat malignant cancers driven by viral oncogenes.Virol J. 2021 Jan 13;18(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01488-1. Virol J. 2021. PMID: 33441159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome Engineering as a Therapeutic Approach in Cancer Therapy: A Comprehensive Review.Adv Genet (Hoboken). 2024 Feb 5;5(1):2300201. doi: 10.1002/ggn2.202300201. eCollection 2024 Mar. Adv Genet (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38465225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reporter Alleles in hiPSCs: Visual Cues on Development and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 13;25(20):11009. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011009. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456792 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

