Eosinophilic esophagitis in Japanese patients: A mild and slow-progressing disorder
- PMID: 30388148
- PMCID: PMC6214552
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206621
Eosinophilic esophagitis in Japanese patients: A mild and slow-progressing disorder
Abstract
Background and aim: Awareness of eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) has gradually increased in Japan, therefore the characteristics of this disease in the Japanese patient population need to be elucidated. This study aimed to investigate the features of EoE in the Japanese population.
Methods: During a 2-year period, all gastrointestinal endoscopies were performed with maximum attention being paid to identify EoE through endoscopic findings. Clinical features and findings were analyzed among this population.
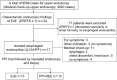
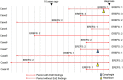
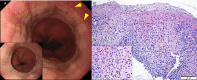
Results: Among a total of 8589 patients (general gastrointestinal endoscopy, performed for evaluation of symptoms or disease follow-up: 3669; medical check-up endoscopy, routinely performed in asymptomatic patients: 4920), 17 patients (0.20%) were diagnosed with esophageal eosinophilia (mean age ± standard deviation: 44±11.9 years; 1 female). Only 6 patients with esophageal eosinophilia were diagnosed by general gastrointestinal endoscopy; among them, 3 patients had dysphagia and 3 were asymptomatic. The remaining 11 patients were diagnosed by medical check-up endoscopy. All patients were treated with a proton pump inhibitor (PPI); 5 were diagnosed with EoE and 12 with PPI responsive esophageal eosinophilia. Chronological endoscopy analysis showed that EoE findings could be observed for a mean of 6.1 years prior to diagnosis, and the disease did not significantly progress in severity.
Conclusions: Most Japanese patients with EoE have mild and slowly progressing disease, which can be diagnosed when close attention is paid to the endoscopic findings. Medical check-up endoscopy in Japan could be a great opportunity for the early diagnosis of EoE.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Similarities and differences among eosinophilic esophagitis, proton-pump inhibitor-responsive esophageal eosinophilia, and reflux esophagitis: comparisons of clinical, endoscopic, and histopathological findings in Japanese patients.J Gastroenterol. 2017 Feb;52(2):203-210. doi: 10.1007/s00535-016-1213-1. Epub 2016 Apr 23. J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 27108416
-
A multicenter study on the prevalence of eosinophilic esophagitis and PPI-responsive esophageal eosinophilic infiltration.Intern Med. 2012;51(23):3235-9. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.51.8670. Epub 2012 Dec 1. Intern Med. 2012. PMID: 23207117
-
[Proton Pump Inhibitor-responsive Esophageal Eosinophilia: An Overview of Cases from One University Hospital Center].Korean J Gastroenterol. 2016 Apr 25;67(4):178-82. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2016.67.4.178. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27112243 Korean.
-
Respiratory symptoms associated with eosinophilic esophagitis.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2018 Nov;53(11):1587-1591. doi: 10.1002/ppul.24168. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2018. PMID: 30238702 Review.
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis: Update in diagnosis and management. Position paper by the Italian Society of Gastroenterology and Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (SIGE).Dig Liver Dis. 2017 Mar;49(3):254-260. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2016.11.012. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Dig Liver Dis. 2017. PMID: 27979389 Review.
Cited by
-
How to approach adult patients with asymptomatic esophageal eosinophilia.Dis Esophagus. 2021 Jan 11;34(1):doaa105. doi: 10.1093/dote/doaa105. Dis Esophagus. 2021. PMID: 33016307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Application of Convolutional Neural Networks for Diagnosis of Eosinophilic Esophagitis Based on Endoscopic Imaging.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 30;11(9):2529. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092529. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566653 Free PMC article.
-
Eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders: a narrative review on clinical perspectives and research gaps in the Asian context.Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Aug 23;9:69. doi: 10.21037/tgh-24-34. eCollection 2024. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 39503038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eosinophilic esophagitis: an interdisciplinary clinical problem.Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021 Feb;38(2):36-42. doi: 10.5114/ada.2019.87237. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2021. PMID: 34408564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Features of Esophageal Eosinophilia According to Endoscopic Phenotypes.Intern Med. 2020 Dec 1;59(23):2971-2979. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.4447-20. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32759578 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

