Microbial Interkingdom Interactions in Roots Promote Arabidopsis Survival
- PMID: 30388454
- PMCID: PMC6218654
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.020
Microbial Interkingdom Interactions in Roots Promote Arabidopsis Survival
Abstract
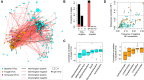
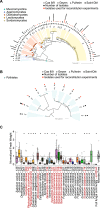
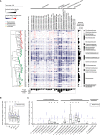
Roots of healthy plants are inhabited by soil-derived bacteria, fungi, and oomycetes that have evolved independently in distinct kingdoms of life. How these microorganisms interact and to what extent those interactions affect plant health are poorly understood. We examined root-associated microbial communities from three Arabidopsis thaliana populations and detected mostly negative correlations between bacteria and filamentous microbial eukaryotes. We established microbial culture collections for reconstitution experiments using germ-free A. thaliana. In plants inoculated with mono- or multi-kingdom synthetic microbial consortia, we observed a profound impact of the bacterial root microbiota on fungal and oomycetal community structure and diversity. We demonstrate that the bacterial microbiota is essential for plant survival and protection against root-derived filamentous eukaryotes. Deconvolution of 2,862 binary bacterial-fungal interactions ex situ, combined with community perturbation experiments in planta, indicate that biocontrol activity of bacterial root commensals is a redundant trait that maintains microbial interkingdom balance for plant health.
Keywords: bacteria; fungi; microbe-microbe interactions; oomycetes; plant microbiota; synthetic microbial communities.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures








References
-
- Bai Y., Müller D.B., Srinivas G., Garrido-Oter R., Potthoff E., Rott M., Dombrowski N., Münch P.C., Spaepen S., Remus-Emsermann M. Functional overlap of the Arabidopsis leaf and root microbiota. Nature. 2015;528:364–369. - PubMed
-
- Bengtsson-Palme J., Ryberg M., Hartmann M., Branco S., Wang Z., Godhe A., De Wit P., Sanchez-Garcia M., Ebersberger I., de Sousa F. Improved software detection and extraction of ITS1 and ITS2 from ribosomal ITS sequences of fungi and other eukaryotes for analysis of environmental sequencing data. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2013;4:914–919.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

