Chronic Ingestion of Sodium and Potassium Bicarbonate, with Potassium, Magnesium and Calcium Citrate Improves Anaerobic Performance in Elite Soccer Players
- PMID: 30388775
- PMCID: PMC6266022
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10111610
Chronic Ingestion of Sodium and Potassium Bicarbonate, with Potassium, Magnesium and Calcium Citrate Improves Anaerobic Performance in Elite Soccer Players
Abstract
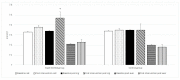
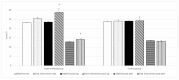
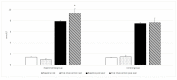
Anaerobic power and anaerobic capacity significantly influence performance in many sport disciplines. These include prolonged sprints in athletics, swimming, or cycling, and other high intensity intermittent sports, such as soccer or basketball. Considering the association of exercise-induced acidosis and fatigue, the ingestion of potential buffering agents such as sodium bicarbonate, has been suggested to attenuate metabolic acidosis and improve anaerobic performance. Since elite soccer players cover from 200 to 350 m while sprinting, performing 40⁻60 all out sprints during a game, it seems that repeated sprint ability in soccer players is among the key components of success. In our experiment, we evaluated the effectiveness of chronic supplementation with sodium and potassium bicarbonate, fortified with minerals, on speed and speed endurance in elite soccer players. Twenty-six soccer players participated in the study. The subjects were randomly divided into two groups. The experimental group was supplemented with sodium bi-carbonate and potassium di-carbonate fortified with minerals, while the control group received a placebo. The athletes were tested at baseline and after nine days of supplementation. Anaerobic performance was evaluated by the Repeated Anaerobic Sprint Test (RAST) protocol which involved 6 × 30 m max sprints, separated by 10 s of active recovery. Resting, post ingestion and post exercise concentrations of HCO₃- and blood pH were measured as well as lactate concentration. The current investigation demonstrated a significant increase in RAST performance of elite soccer players supplemented with sodium and potassium bicarbonate along with calcium phosphate, potassium citrate, and magnesium citrate ingested twice a day over a nine-day training period. The improvements in anaerobic performance were caused by increased resting blood pH and bicarbonate levels.
Keywords: buffering; speed endurance; supplementation; team sport athletes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The Ministry of Science and Higher Education of Poland had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Effects of Long-Term Magnesium Creatine Chelate Supplementation on Repeated Sprint Ability (RAST) in Elite Soccer Players.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 28;12(10):2961. doi: 10.3390/nu12102961. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32998206 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Pre-exercise Sodium Citrate Ingestion on Repeated Sprint Performance in Soccer Players.J Strength Cond Res. 2024 Mar 1;38(3):556-562. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000004651. Epub 2024 Jan 19. J Strength Cond Res. 2024. PMID: 38241467 Clinical Trial.
-
Sodium Bicarbonate Supplementation Does Not Improve Running Anaerobic Sprint Test Performance in Semiprofessional Adolescent Soccer Players.Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2020 Sep 1;30(5):330-337. doi: 10.1123/ijsnem.2020-0031. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab. 2020. PMID: 32668408 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Creatine Supplementation on Athletic Performance in Soccer Players: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2019 Mar 31;11(4):757. doi: 10.3390/nu11040757. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30935142 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary and Ergogenic Supplementation to Improve Elite Soccer Players' Performance.Ann Nutr Metab. 2021;77(4):197-203. doi: 10.1159/000516397. Epub 2021 Jun 11. Ann Nutr Metab. 2021. Retraction in: Ann Nutr Metab. 2024;80(3):171. doi: 10.1159/000538351. PMID: 34120108 Retracted. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of dietary supplements on athletic performance in elite soccer players: a systematic review.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023 Dec;20(1):2236060. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2023.2236060. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37462346 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of magnesium supplementation on muscle soreness in different type of physical activities: a systematic review.J Transl Med. 2024 Jul 5;22(1):629. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05434-x. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38970118 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of Injuries in Men's Professional and Amateur Football (Part I).J Clin Med. 2023 Aug 26;12(17):5569. doi: 10.3390/jcm12175569. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37685638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of serial and acute enteric-coated sodium bicarbonate supplementation on anaerobic performance, physiological profile, and metabolomics in healthy young men.Front Nutr. 2022 Aug 16;9:931671. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.931671. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 36051902 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Ingestion of Bicarbonate-Rich Water Improves Anaerobic Performance in Hypohydrated Elite Judo Athletes: A Pilot Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 6;18(9):4948. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18094948. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34066531 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

