A Systems-Level Analysis of Mechanisms of Platycodon grandiflorum Based on A Network Pharmacological Approach
- PMID: 30388815
- PMCID: PMC6278259
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23112841
A Systems-Level Analysis of Mechanisms of Platycodon grandiflorum Based on A Network Pharmacological Approach
Abstract
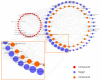
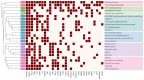
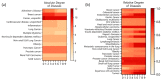
Platycodon grandiflorum (PG) is widely used in Asia for its various beneficial effects. Although many studies were conducted to understand the molecular mechanisms of PG, it is still unclear how the combinations of multiple ingredients work together to exert its therapeutic effects. The aim of the present study was to provide a comprehensive review of the systems-level mechanisms of PG by adopting network pharmacological analysis. We constructed a compound⁻target⁻disease network for PG using experimentally validated and machine-leaning-based prediction results. Each target of the network was analyzed based on previously known pharmacological activities of PG. Gene ontology analysis revealed that the majority of targets were related to cellular and metabolic processes, responses to stimuli, and biological regulation. In pathway enrichment analyses of targets, the terms related to cancer showed the most significant enrichment and formed distinct clusters. Degree matrix analysis for target⁻disease associations of PG suggested the therapeutic potential of PG in various cancers including hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric cancer, prostate cancer, small-cell lung cancer, and renal cell carcinoma. We expect that network pharmacological approaches will provide an understanding of the systems-level mechanisms of medicinal herbs and further develop their therapeutic potentials.
Keywords: Kilkyung; Platycodon grandiflorum; network pharmacology; systems-level mechanism; traditional Asian medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Jang K.J., Kim H.K., Han M.H., Oh Y.N., Yoon H.M., Chung Y.H., Kim G.Y., Hwang H.J., Kim B.W., Choi Y.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of saponins derived from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorus in lipopolysaccharidestimulated BV2 microglial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013;31:1357–1366. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2013.1330. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahn K.S., Noh E.J., Zhao H.L., Jung S.H., Kang S.S., Kim Y.S. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase II by Platycodon grandiflorum saponins via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells. Life Sci. 2005;76:2315–2328. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.10.042. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Choi J.H., Hwang Y.P., Kim H.G., Khanal T., Do M.T., Jin S.W., Han H.J., Lee H.S., Lee Y.C., Chung Y.C., et al. Saponins from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum suppresses TGFbeta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via repression of PI3K/Akt, ERK1/2 and Smad2/3 pathway in human lung carcinoma A549 cells. Nutr. Cancer. 2014;66:140–151. doi: 10.1080/01635581.2014.853087. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

