In vivo administration of recombinant BTNL2-Fc fusion protein ameliorates graft-versus-host disease in mice
- PMID: 30389093
- PMCID: PMC6368466
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2018.10.008
In vivo administration of recombinant BTNL2-Fc fusion protein ameliorates graft-versus-host disease in mice
Abstract
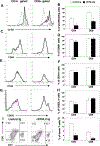
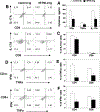
Although hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has been widely used in the treatment of many diseases, graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) remains a major complication after allogeneic HSCT. Butyrophilin-like 2 (BTNL2) protein has been reported to have the ability to inhibit T cell proliferation in vitro; its ability to inhibit T cell responses in vivo has not been determined. We show here that in vivo administration of recombinant BTNL2-IgG2a Fc (rBTNL2-Ig) fusion protein ameliorates GVHD in mice. This is related to the ability of rBTNL2-Ig to inhibit T cell proliferation, activation and Th1/Th17 cytokine production in vivo. Furthermore, rBTNL2-Ig treatment increases the generation of regulatory T cells. Our results suggest that rBTNL2-Ig has the potential to be used in the prevention and treatment of patients with GVHD.
Keywords: Activation; Butyrophilin-like 2; Graft-versus-host disease; Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; Regulatory T cells; T cell proliferation.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
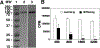
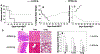
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

