Effect of Statins on Renal Function in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
- PMID: 30390007
- PMCID: PMC6215008
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34632-z
Effect of Statins on Renal Function in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Abstract
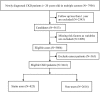
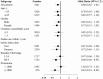
Dyslipidemia is associated with glomerular injury. However, the effect of statins on chronic kidney disease (CKD) progression remains controversial. We aimed to investigate the efficacy of statins for renal protection in patients with CKD. The retrospective cohort study comprised 3441 patients diagnosed with CKD in multiple medical centers. We divided the patients into two cohorts based on statin prescription, and compared proportions and risks of CKD progression events between the two groups. CKD progression event was defined as an average annual decline of eGFR >5 mL/min/1.73 m2 or advancement to the dialysis stage. The result revealed that among all incident patients with CKD, 28.7% and 30.3% of the users and nonusers demonstrated CKD progression, respectively. The crude odds ratio (OR) of CKD progression was 0.93 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.78-1.10]. After adjustment for baseline characteristics, the adjusted OR was 0.80 (95% CI 0.63-1.01). The sensitivity analysis results showed consistent OR for CKD progression, stratification by age, sex, Charlson score, and statins use within 1 year before index date. The effect of statins was significant in patients with CKD stage 3B-5 (OR 0.68, 95% CI 0.48-0.95), but not statistically significant in those with CKD stage 1-3A (OR 0.97, 95% CI 0.68-1.38). The effect of statins was significant in patients with proteinuria ≥1000 mg/day (OR 0.63, 95% CI 0.43-0.92), but not statistically significant in those with proteinuria <1000 mg/day (OR 1.02, 95% CI 0.74-1.41).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of atorvastatin on renal function in patients with dyslipidemia and chronic kidney disease: assessment of clinical usefulness in CKD patients with atorvastatin (ASUCA) trial.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017 Jun;21(3):417-424. doi: 10.1007/s10157-016-1304-6. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 27392909 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Association of Statin Use With Kidney Damage and Function Among HIV-Infected Men.J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019 Oct 1;82(2):202-210. doi: 10.1097/QAI.0000000000002122. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2019. PMID: 31356467 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of dyslipidemia in chronic kidney disease.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2014 Apr;18(2):185-8. doi: 10.1007/s10157-013-0891-8. Epub 2014 Jan 11. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24408220 Review.
-
[Effect of statins on renal function].Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2013;55(7):1295-300. Nihon Jinzo Gakkai Shi. 2013. PMID: 24288966 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Using pharmacists to improve risk stratification and management of stage 3A chronic kidney disease: a feasibility study.BMC Nephrol. 2016 Nov 8;17(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12882-016-0383-7. BMC Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 27825313 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Characteristics of Dyslipidemia in Primary Nephrotic Syndromes.Cureus. 2025 May 14;17(5):e84077. doi: 10.7759/cureus.84077. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40519478 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blockade and Statins on Kidney Injury Marker 1 (KIM-1) in Female Rats Receiving L-NAME and Angiotensin II.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 30;24(7):6500. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076500. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047470 Free PMC article.
-
Association between baseline LDL-C and prognosis among patients with coronary artery disease and advanced kidney disease.BMC Nephrol. 2021 May 6;22(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02375-1. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33957880 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Accumulation and Chronic Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2019 Mar 28;11(4):722. doi: 10.3390/nu11040722. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30925738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of pleiotropic effects of statins vs fibrates on laboratory parameters in patients with dyslipidemia: A retrospective cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Dec 11;99(50):e23427. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023427. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33327270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- System, U. S. R. D. 2017 USRDS annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, Bethesda, MD, https://www.usrds.org/adr.aspx 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous