Integrative regulation of physiology by histone deacetylase 3
- PMID: 30390028
- PMCID: PMC6347506
- DOI: 10.1038/s41580-018-0076-0
Integrative regulation of physiology by histone deacetylase 3
Abstract
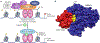
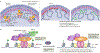
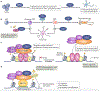
Cell-type-specific gene expression is physiologically modulated by the binding of transcription factors to genomic enhancer sequences, to which chromatin modifiers such as histone deacetylases (HDACs) are recruited. Drugs that inhibit HDACs are in clinical use but lack specificity. HDAC3 is a stoichiometric component of nuclear receptor co-repressor complexes whose enzymatic activity depends on this interaction. HDAC3 is required for many aspects of mammalian development and physiology, for example, for controlling metabolism and circadian rhythms. In this Review, we discuss the mechanisms by which HDAC3 regulates cell type-specific enhancers, the structure of HDAC3 and its function as part of nuclear receptor co-repressors, its enzymatic activity and its post-translational modifications. We then discuss the plethora of tissue-specific physiological functions of HDAC3.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
M.A.L. is a consultant to KDAC, a company developing his-tone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors, and Novartis, and serves on scientific advisory boards for Pfizer and Eli Lilly and Co.
Figures



References
-
- Spitz F & Furlong EEM Transcription factors: from enhancer binding to developmental control. Nat. Rev. Genet 13, 613–626 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Carroll JS et al. Chromosome-wide mapping of estrogen receptor binding reveals long-range regulation requiring the forkhead protein FoxA1. Cell 122, 33–43 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

