Expression of novel proteins by polyomaviruses and recent advances in the structural and functional features of agnoprotein of JC virus, BK virus, and simian virus 40
- PMID: 30390301
- PMCID: PMC6395527
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.27715
Expression of novel proteins by polyomaviruses and recent advances in the structural and functional features of agnoprotein of JC virus, BK virus, and simian virus 40
Abstract
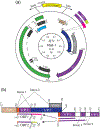
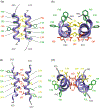
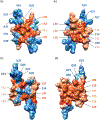
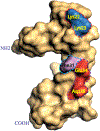
Polyomavirus family consists of a highly diverse group of small DNA viruses. The founding family member (MPyV) was first discovered in the newborn mouse in the late 1950s, which induces solid tumors in a wide variety of tissue types that are the epithelial and mesenchymal origin. Later, other family members were also isolated from a number of mammalian, avian and fish species. Some of these viruses significantly contributed to our current understanding of the fundamentals of modern biology such as transcription, replication, splicing, RNA editing, and cell transformation. After the discovery of first two human polyomaviruses (JC virus [JCV] and BK virus [BKV]) in the early 1970s, there has been a rapid expansion in the number of human polyomaviruses in recent years due to the availability of the new technologies and brought the present number to 14. Some of the human polyomaviruses cause considerably serious human diseases, including progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, polyomavirus-associated nephropathy, Merkel cell carcinoma, and trichodysplasia spinulosa. Emerging evidence suggests that the expression of the polyomavirus genome is more complex than previously thought. In addition to encoding universally expressed regulatory and structural proteins (LT-Ag, Sm t-Ag, VP1, VP2, and VP3), some polyomaviruses express additional virus-specific regulatory proteins and microRNAs. This review summarizes the recent advances in polyomavirus genome expression with respect to the new viral proteins and microRNAs other than the universally expressed ones. In addition, a special emphasis is devoted to the recent structural and functional discoveries in the field of polyomavirus agnoprotein which is expressed only by JCV, BKV, and simian virus 40 genomes.
Keywords: Agnoprotein; BKV; DNA replication; Merkel cell carcinoma polyomavirus; NMR; SV40; dimer and oligomer formation; polyomavirus JCV; progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy; transcription and viroporin.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery and characterization of novel trans-spliced products of human polyoma JC virus late transcripts from PML patients.J Cell Physiol. 2018 May;233(5):4137-4155. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26219. Epub 2017 Dec 18. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29044559 Free PMC article.
-
[New, newer, newest human polyomaviruses: how far?].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2013 Apr;47(2):362-81. doi: 10.5578/mb.5377. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2013. PMID: 23621738 Review. Turkish.
-
Recent advances in discovery and functional analysis of the small proteins and microRNA expressed by polyomaviruses.Virology. 2025 Jan;602:110310. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2024.110310. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Virology. 2025. PMID: 39612622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural evaluation of new human polyomaviruses provides clues to pathobiology.Trends Microbiol. 2010 May;18(5):215-23. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Feb 20. Trends Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20176487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High expression of JC polyomavirus-encoded microRNAs in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy tissues and its repressive role in virus replication.PLoS Pathog. 2020 Apr 23;16(4):e1008523. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008523. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32324824 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association Between Simian Virus 40 and Human Tumors.Front Oncol. 2019 Jul 25;9:670. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00670. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31403031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Domains of the Early Proteins and Experimental and Epidemiological Studies Suggest a Role for the Novel Human Polyomaviruses in Cancer.Front Microbiol. 2022 Feb 18;13:834368. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.834368. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35250950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human neurotropic polyomavirus, JC virus, agnoprotein targets mitochondrion and modulates its functions.Virology. 2021 Jan 15;553:135-153. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2020.11.004. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Virology. 2021. PMID: 33278736 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular Transmission of Naked Viruses through Extracellular Vesicles: Focus on Polyomaviruses.Viruses. 2020 Sep 26;12(10):1086. doi: 10.3390/v12101086. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32993049 Free PMC article. Review.
-
G-Quadruplexes in the Regulation of Viral Gene Expressions and Their Impacts on Controlling Infection.Pathogens. 2024 Jan 8;13(1):60. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13010060. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38251367 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akhbari P, Tobin D, Poterlowicz K, Roberts W, & Boyne JR (2018). MCV‐miR‐M1 targets the host‐cell immune response resulting in the attenuation of neutrophil chemotaxis. Journal of Investigative Dermatology, 138, 2343–2354. - PubMed
-
- Alcamí A, Symons JA, Collins PD, Williams TJ, & Smith GL (1998). Blockade of chemokine activity by a soluble chemokine binding protein from vaccinia virus. Journal of Immunology, 160(2), 624–633. - PubMed
-
- Al‐Mohanna F, Parhar R, & Kotwal GJ (2001). Vaccinia virus complement control protein is capable of protecting xenoendothelial cells from antibody binding and killing by human complement and cytotoxic cells. Transplantation, 71(6), 796–801. - PubMed

