From single cells to tissue self-organization
- PMID: 30390414
- PMCID: PMC6519261
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.14694
From single cells to tissue self-organization
Abstract
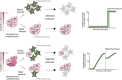
Self-organization is a process by which interacting cells organize and arrange themselves in higher order structures and patterns. To achieve this, cells must have molecular mechanisms to sense their complex local environment and interpret it to respond accordingly. A combination of cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic cues are decoded by the single cells dictating their behaviour, their differentiation and symmetry-breaking potential driving development, tissue remodeling and regenerative processes. A unifying property of these self-organized pattern-forming systems is the importance of fluctuations, cell-to-cell variability, or noise. Cell-to-cell variability is an inherent and emergent property of populations of cells that maximize the population performance instead of the individual cell, providing tissues the flexibility to develop and maintain homeostasis in diverse environments. In this review, we will explore the role of self-organization and cell-to-cell variability as fundamental properties of multicellularity-and the requisite of single-cell resolution for its understanding. Moreover, we will analyze how single cells generate emergent multicellular dynamics observed at the tissue level 'travelling' across different scales: spatial, temporal and functional.
Keywords: cell-to-cell variability; crossing-scales technologies; development; emergent properties; multicellularity; organoids; pattern formation; regeneration; self-organization; symmetry-breaking.
© 2018 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Engineering Stem Cell Self-organization to Build Better Organoids.Cell Stem Cell. 2019 Jun 6;24(6):860-876. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2019.05.005. Cell Stem Cell. 2019. PMID: 31173716 Review.
-
Mechanochemical Interplay Drives Polarization in Cellular and Developmental Systems.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016;116:633-57. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2015.11.039. Epub 2016 Jan 20. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2016. PMID: 26970646 Review.
-
Quantitative multivariate analysis of dynamic multicellular morphogenic trajectories.Integr Biol (Camb). 2015 Jul;7(7):825-33. doi: 10.1039/c5ib00072f. Integr Biol (Camb). 2015. PMID: 26095427 Free PMC article.
-
A conceptual model of morphogenesis and regeneration.Acta Biotheor. 2015 Sep;63(3):283-94. doi: 10.1007/s10441-015-9249-9. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Acta Biotheor. 2015. PMID: 25822060 Free PMC article.
-
Towards organogenesis and morphogenesis in vitro: harnessing engineered microenvironment and autonomous behaviors of pluripotent stem cells.Integr Biol (Camb). 2018 Oct 15;10(10):574-586. doi: 10.1039/c8ib00116b. Integr Biol (Camb). 2018. PMID: 30225509 Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting cancer stages from tissue energy dissipation.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 23;13(1):15894. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-42780-0. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37741864 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity of High-Grade Gliomas: From Disease Biology to Therapeutic Implications.Front Oncol. 2021 Aug 5;11:703764. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.703764. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34422657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiscale light-sheet organoid imaging framework.Nat Commun. 2022 Aug 18;13(1):4864. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-32465-z. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35982061 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term live imaging and multiscale analysis identify heterogeneity and core principles of epithelial organoid morphogenesis.BMC Biol. 2021 Feb 24;19(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12915-021-00958-w. BMC Biol. 2021. PMID: 33627108 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Spheroid Development Under Flow Conditions with Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells in a 3D Porous Hydrogel Supplemented with Hydroxyapatite.Gels. 2024 Oct 18;10(10):666. doi: 10.3390/gels10100666. Gels. 2024. PMID: 39451319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herr P, Hausmann G & Basler K (2012) WNT secretion and signalling in human disease. Trends Mol Med 18, 483–493. - PubMed
-
- Clevers H & Nusse R (2012) Wnt/beta‐catenin signaling and disease. Cell 149, 1192–1205. - PubMed
-
- Wennekamp S, Mesecke S, Nédélec F & Hiiragi T (2013) A self‐organization framework for symmetry breaking in the mammalian embryo. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 14, 452–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

