Effects of music intervention during caesarean delivery on anxiety and stress of the mother a controlled, randomised study
- PMID: 30390639
- PMCID: PMC6215648
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-018-2069-6
Effects of music intervention during caesarean delivery on anxiety and stress of the mother a controlled, randomised study
Abstract
Background: Stress and anxiety during pregnancy and childbirth have negative consequences for both mother and child. There are indications that music has a positive effect in this situation. The present study investigates the influence of music during the caesarean on anxiety and stress of the expectant mother.
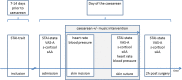
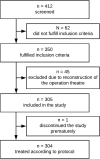
Methods: The SAMBA study is a single-centre, controlled, randomized study including 304 patients. Women in the intervention group heard music via loudspeakers from one of four self-selected genres. The control group had standard treatment without music. The caesarean was performed in regional Anesthesia. At admission, at skin incision, during skin suture and two hours after completion of surgery, different subjective (State-Trait Anxiety Inventory, visual analogue scale for anxiety) and objective parameters (salivary cortisol/amylase, heart rate, blood pressure) were collected. Mixed-factorial Analysis of variances as well as independent sample t-tests were applied for data analysis.
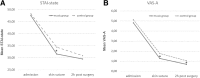
Results: At skin suture, significantly lower anxiety levels were reported in the intervention group regarding State anxiety (31.56 vs. 34.41; p = .004) and visual analogue scale for anxiety (1.27 vs. 1.76; p = .018). Two hours after surgery, the measured visual analogue scale for anxiety score in the intervention group was still significantly lower (0.69 vs. 1.04; p = .018). The objective parameters showed significant differences between the groups in salivary cortisol increase from admission to skin suture (12.29 vs. 16.61 nmol/L; p = .043), as well as systolic blood pressure (130.11 vs. 136.19 mmHg; p = .002) and heart rate (88.40 vs. 92.57/min; p = .049) at skin incision.
Conclusions: Music during caesarean is an easy implementable and effective way of reducing stress and anxiety of the expectant mother.
Trial registration: German registry for clinical trials ( DRKS00007840 ). Registered 16/06/2015. Retrospectively registered.
Keywords: Anxiety; Caesarean; Music intervention; Stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of the Medical Department of the Heinrich-Heine-University in Dusseldorf (No.: 3625). The research was conducted in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration. All patients gave their written consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The effects of a music intervention during port catheter placement on anxiety and stress.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 11;11(1):5807. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85139-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33707520 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of prenatal music stimulation on state/trait anxiety in full-term pregnancy and its influence on childbirth: a randomized controlled trial.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018 Apr;31(8):1058-1065. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2017.1306511. Epub 2017 Apr 3. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018. PMID: 28287005 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Music during Multiple Cesarean Section Delivery.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2018 Mar;28(3):247-249. doi: 10.29271/jcpsp.2018.03.247. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2018. PMID: 29544589 Clinical Trial.
-
Systematic review on music interventions during pregnancy in favor of the well-being of mothers and eventually their offspring.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2024 Aug;6(8):101400. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2024.101400. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2024. PMID: 38866136
-
Effects of music therapy on anxiety and physiologic parameters in angiography: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Neurointerv Surg. 2019 Apr;11(4):416-423. doi: 10.1136/neurintsurg-2018-014313. Epub 2018 Nov 10. J Neurointerv Surg. 2019. PMID: 30415224
Cited by
-
Effect of music interventions on anxiety during labor: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.PeerJ. 2019 May 15;7:e6945. doi: 10.7717/peerj.6945. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31143552 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the effect of intraoperative tropisetron on postoperative rebound pain after brachial plexus block: a randomized controlled trial.Pain Rep. 2024 May 15;9(3):e1163. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000001163. eCollection 2024 Jun. Pain Rep. 2024. PMID: 38756786 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of a music and singing intervention during pregnancy on maternal well-being and mother-infant bonding: a randomised, controlled study.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2021 Jan;303(1):69-83. doi: 10.1007/s00404-020-05727-8. Epub 2020 Aug 10. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2021. PMID: 32776296 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effectiveness of Music on Perinatal Anxiety Among Pregnant Women and Newborn Behaviors: A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis.Indian J Psychol Med. 2023 Nov;45(6):565-572. doi: 10.1177/02537176231167077. Epub 2023 May 6. Indian J Psychol Med. 2023. PMID: 38545536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effects of a music intervention during port catheter placement on anxiety and stress.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 11;11(1):5807. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85139-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33707520 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.

