Serum neurofilament light levels correlate with severity measures and neurodegeneration markers in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 30390718
- PMCID: PMC6215337
- DOI: 10.1186/s13195-018-0439-y
Serum neurofilament light levels correlate with severity measures and neurodegeneration markers in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Background: Biomarkers that can track disease onset and progression in autosomal dominant Alzheimer's disease (ADAD) are needed. We investigate whether serum neurofilament light (NfL) concentration is associated with clinical and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) markers in ADAD. We also evaluate serum NfL differences between clinical groups.
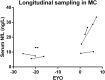
Methods: Serum NfL was measured cross-sectionally in 60 individuals from ADAD families using an ultrasensitive immunoassay on the Single molecule array (Simoa) platform and longitudinally in an exploratory study in a subset of six mutation carriers. Spearman coefficients assessed associations between serum NfL and relevant measures. Differences between groups were evaluated by Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests.
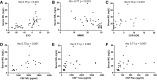
Results: Forty-two participants were mutation carriers: 22 symptomatic (SMC) and 20 asymptomatic (AMC). Eighteen subjects were non-carriers and cognitively normal (controls (CTR)). Serum NfL correlated with the estimated years from symptoms onset across mutation carriers (rho = 0.75, p < 0.001). In mutation carriers, serum NfL also showed strong correlation with clinical (rho = 0.70, p < 0.001) and cognitive (rho = -0.77, p < 0.001) measures and CSF NfL, total tau and phosphorylated tau levels (rho = 0.72, 0.71, and 0.71, respectively, all p < 0.001). Serum NfL concentration was higher in SMC than in AMC and CTR.
Conclusions: Serum NfL might be a feasible non-invasive biomarker to track disease onset and severity in ADAD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Biomarkers; Familial Alzheimer’s disease; Neurofilament light; Presenilin 1.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Hospital Clinic of Barcelona ethics committee (HCB/2012/7476) and all subjects gave written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
HZ has served on advisory boards for Roche Diagnostics and Eli Lilly, has received travel support from Teva, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB, a GU Ventures-based platform company at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden. NCF has received fees (paid to University College London) for consultancy from Eli Lilly, Novartis, Sanofi, Roche/Genentech, and GlaxoSmithKline, and for serving on a Data Monitoring Committee for Biogen. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

