Revisiting dispersible milk-drug tablets as a solid lipid formulation in the context of digestion
- PMID: 30391337
- PMCID: PMC6328708
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.10.069
Revisiting dispersible milk-drug tablets as a solid lipid formulation in the context of digestion
Abstract
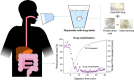
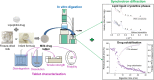
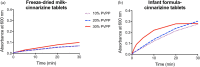
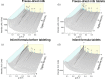
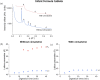
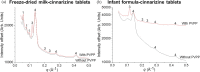
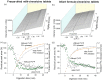
Oral delivery of dispersible tablets is a preferred route of administration for paediatrics due to ease of administration and dose control. Milk has gained interest as a drug delivery system due to its ability to dissolve poorly water-soluble drugs. There are no reports of milk tablet formulations being assessed in the context of lipid digestion, which is critical in influencing orally administered drug solubility and bioavailability. Milk-drug tablets were formulated by blending freeze-dried bovine milk or infant formula with the poorly water-soluble drug cinnarizine, which were directly compressed. Tablet strength, friability and dispersibility were quantified and synchrotron X-ray scattering was used to determine the lipid liquid crystalline phases formed during in vitro digestion of dispersed tablets and their effects on drug solubilisation. Tableting had a significant impact on the self-assembly of lipids in redispersed milk tablets whereas no effect was seen for infant formula tablets. Incorporation of the disintegrant poly(vinylpolypyrrolidone) to reduce tablet dispersion times promoted the formation of hexagonal liquid crystalline phases upon digestion but had minimal effect on drug solubilisation. These findings show that similar to the use of liquid milk, the formulation of milk-drug tablets can be used to improve solubilisation of poorly water-soluble drugs.
Keywords: Dispersible tablet; Drug solubilisation; In vitro digestion; Milk; Self-assembly; X-ray scattering.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Solubilisation behaviour of poorly water-soluble drugs during digestion of solid SMEDDS.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018 Sep;130:236-246. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2018.07.006. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2018. PMID: 29981444
-
A lipid-based liquid crystalline matrix that provides sustained release and enhanced oral bioavailability for a model poorly water soluble drug in rats.Int J Pharm. 2007 Aug 1;340(1-2):52-60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2007.03.020. Epub 2007 Mar 24. Int J Pharm. 2007. PMID: 17467935
-
Phytantriol and glyceryl monooleate cubic liquid crystalline phases as sustained-release oral drug delivery systems for poorly water-soluble drugs II. In-vivo evaluation.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010 Jul;62(7):856-65. doi: 10.1211/jpp.62.06.0006. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20636873
-
50years of oral lipid-based formulations: Provenance, progress and future perspectives.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Jun 1;101:167-194. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2016.04.007. Epub 2016 Apr 16. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 27089810 Review.
-
Critical In Vitro Characterization Methods of Lipid-Based Formulations for Oral Delivery: a Comprehensive Review.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018 Dec 19;20(1):16. doi: 10.1208/s12249-018-1239-1. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2018. PMID: 30569266 Review.
Cited by
-
Small-volume in vitro lipid digestion measurements for assessing drug dissolution in lipid-based formulations using SAXS.Int J Pharm X. 2022 Feb 9;4:100113. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpx.2022.100113. eCollection 2022 Dec. Int J Pharm X. 2022. PMID: 35243327 Free PMC article.
-
Milk Oral Lyophilizates with Loratadine: Screening for New Excipients for Pediatric Use.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jun 24;14(7):1342. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071342. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35890238 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of Self-Assembled Mesophases During Lipid Digestion.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 11;9:657886. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.657886. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34178984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Correlating Digestion-Driven Self-Assembly in Milk and Infant Formulas with Changes in Lipid Composition.ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020 May 18;3(5):3087-3098. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.0c00131. Epub 2020 May 4. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2020. PMID: 32455340 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of pasteurization on the self-assembly of human milk lipids during digestion.J Lipid Res. 2022 May;63(5):100183. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2022.100183. Epub 2022 Feb 16. J Lipid Res. 2022. PMID: 35181315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Christie W.W., Clapperton J.L. Structures of the triglycerides of cows' milk, fortified milks (including. infant formulae), and human milk. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 1982;35(1):22–24.
-
- Clulow A.J., Salim M., Hawley A., Boyd B.J. A closer look at the behaviour of milk lipids during digestion. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2018;211:107–116. - PubMed
-
- Davies E.H., Tuleu C. Medicines for Children: a Matter of Taste. J. Pediatr. 2008;153(5):599–604. - PubMed
-
- Feeney O.M., Crum M.F., McEvoy C.L., Trevaskis N.L., Williams H.D., Pouton C.W. 50 years of oral lipid-based formulations: provenance, progress and future perspectives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016;101:167–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

