Bootstrapping the out-of-sample predictions for efficient and accurate cross-validation
- PMID: 30393425
- PMCID: PMC6191021
- DOI: 10.1007/s10994-018-5714-4
Bootstrapping the out-of-sample predictions for efficient and accurate cross-validation
Abstract
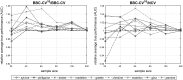
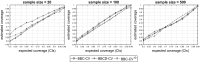
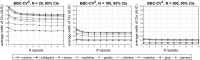
Cross-Validation (CV), and out-of-sample performance-estimation protocols in general, are often employed both for (a) selecting the optimal combination of algorithms and values of hyper-parameters (called a configuration) for producing the final predictive model, and (b) estimating the predictive performance of the final model. However, the cross-validated performance of the best configuration is optimistically biased. We present an efficient bootstrap method that corrects for the bias, called Bootstrap Bias Corrected CV (BBC-CV). BBC-CV's main idea is to bootstrap the whole process of selecting the best-performing configuration on the out-of-sample predictions of each configuration, without additional training of models. In comparison to the alternatives, namely the nested cross-validation (Varma and Simon in BMC Bioinform 7(1):91, 2006) and a method by Tibshirani and Tibshirani (Ann Appl Stat 822-829, 2009), BBC-CV is computationally more efficient, has smaller variance and bias, and is applicable to any metric of performance (accuracy, AUC, concordance index, mean squared error). Subsequently, we employ again the idea of bootstrapping the out-of-sample predictions to speed up the CV process. Specifically, using a bootstrap-based statistical criterion we stop training of models on new folds of inferior (with high probability) configurations. We name the method Bootstrap Bias Corrected with Dropping CV (BBCD-CV) that is both efficient and provides accurate performance estimates.
Keywords: Bias correction; Cross-validation; Hyper-parameter optimization; Performance estimation.
Figures
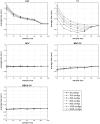
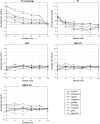
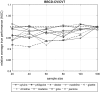
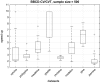
References
-
- Adamou, M., Antoniou, G., Greasidou, E., Lagani, V., Charonyktakis, P., Tsamardinos, I., & Doyle, M. Towards automatic risk assessment to support suicide prevention. Crisis (to appear) - PubMed
-
- Adamou, M., Antoniou, G., Greasidou, E., Lagani, V., Charonyktakis, P., Tsamardinos, I., & Doyle, M. (2018). Mining free-text medical notes for suicide risk assessment. In: Proceedings of the 10th hellenic conference on artificial intelligence, SETN 2018, Patras, Greece, July 9-15, 2018. ACM.
-
- Akaike H. A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control. 1974;19(6):716–723. doi: 10.1109/TAC.1974.1100705. - DOI
-
- Borboudakis G, Stergiannakos T, Frysali M, Klontzas E, Tsamardinos I, Froudakis GE. Chemically intuited, large-scale screening of MOFs by machine learning techniques. npj Computational Materials. 2017;3(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s41524-017-0045-8. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
