PAQR3 inhibits proliferation via suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 30393483
- PMCID: PMC6209724
- DOI: 10.5114/aoms.2017.72220
PAQR3 inhibits proliferation via suppressing PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Introduction: Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases. PAQR (progestin and adipoQ receptor family) 3, a Golgi-anchored membrane protein, has been demonstrated to act as a tumor suppressor in multiple cancers. However, the expression and role of PAQR3 have never been explored in NSCLC. The purpose of this study was to investigate the expression and role of PAQR3 in NSCLC.
Material and methods: Expression of PAQR3 at mRNA and protein levels was determined by qRT-PCR and western blot, respectively. Cell proliferation was analyzed by MTT assay. Apoptosis and cell cycle distribution were evaluated by flow cytometry.
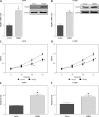
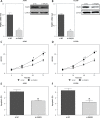
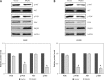
Results: The expression of PAQR3 was downregulated in NSCLC tissue samples and cell lines at both mRNA and protein levels (p < 0.05). Overexpression of PAQR3 significantly inhibited cell proliferation, induced apoptosis and promoted cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase in NSCLC cell lines (p < 0.05). In contrast, knockdown of PAQR3 showed a reverse effect on NSCLC cells (p < 0.05). Moreover, PAQR3 may exert its tumor suppressive roles via suppressing the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in NSCLC.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that PAQR3 is a tumor suppressor in the development of NSCLC and may serve as a novel therapeutic target in the treatment of patients with NSCLC.
Keywords: NSCLC; PAQR3; PI3K/AKT; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
PAQR3 Inhibits Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Growth by Regulating the NF-κB/p53/Bax Axis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 6;8:581919. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.581919. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33123538 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the Golgi scaffold protein PAQR3, and its role in tumor suppression and metabolic pathway compartmentalization.Cancer Manag Res. 2020 Jan 16;12:353-362. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S210919. eCollection 2020. Cancer Manag Res. 2020. PMID: 32021448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAQR3 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion in human glioma cells.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Aug;92:24-32. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.05.046. Epub 2017 May 18. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28528182
-
PAQR3: a novel tumor suppressor gene.Am J Cancer Res. 2015 Aug 15;5(9):2562-8. eCollection 2015. Am J Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26609468 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAQR3 Inhibits the Proliferation and Tumorigenesis in Esophageal Cancer Cells.Oncol Res. 2017 May 24;25(5):663-671. doi: 10.3727/096504016X14761384026719. Oncol Res. 2017. PMID: 28548040 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MiR-345-5p inhibits tumorigenesis of papillary thyroid carcinoma by targeting SETD7.Arch Med Sci. 2019 Mar 25;16(4):888-897. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2019.83823. eCollection 2020. Arch Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 32542092 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of PAQR3 expression predicts poor prognosis of patients with pan-cancer: a meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2025 May 5;15:1574150. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1574150. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40391162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of the PIK3CA, AKT, and PTEN mutations in oral squamous cell carcinoma: literature review.Arch Med Sci. 2020 Nov 13;17(1):207-217. doi: 10.5114/aoms.2020.100780. eCollection 2021. Arch Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33488873 Free PMC article.
-
Golgi Complex: A Signaling Hub in Cancer.Cells. 2022 Jun 21;11(13):1990. doi: 10.3390/cells11131990. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35805075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAQR3 Inhibits Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Growth by Regulating the NF-κB/p53/Bax Axis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 6;8:581919. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.581919. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33123538 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87–108. - PubMed
-
- Koudelakova V, Kneblova M, Trojanec R, Drabek J, Hajduch M. Non-small cell lung cancer: genetic predictors. Biomedical papers of the Medical Faculty of the University Palacky, Olomouc, Czechoslovakia. 2013;157:125–36. - PubMed
-
- Ramnath N, Dilling TJ, Harris LJ, et al. Treatment of stage III non-small cell lung cancer: diagnosis and management of lung cancer, 3rded: American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. Chest. 2013;143(5 Suppl):e314S–40S. - PubMed
-
- Tang YT, Hu T, Arterburn M, et al. PAQR proteins: a novel membrane receptor family defined by an ancient 7-transmembrane pass motif. J Mol Evol. 2005;61:372–80. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
