Real Time Forecasting of Measles Using Generation-dependent Mathematical Model in Japan, 2018
- PMID: 30393578
- PMCID: PMC6198657
- DOI: 10.1371/currents.outbreaks.3cc277d133e2d6078912800748dbb492
Real Time Forecasting of Measles Using Generation-dependent Mathematical Model in Japan, 2018
Abstract
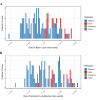
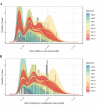
Background: Japan experienced a multi-generation outbreak of measles from March to May, 2018. The present study aimed to capture the transmission dynamics of measles by employing a simple mathematical model, and also forecast the future incidence of cases.
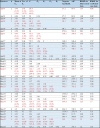
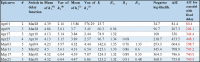
Methods: Epidemiological data that consist of the date of illness onset and the date of laboratory confirmation were analysed. A functional model that captures the generation-dependent growth patterns of cases was employed, while accounting for the time delay from illness onset to diagnosis.
Results: As long as the number of generations is correctly captured, the model yielded a valid forecast of measles cases, explicitly addressing the reporting delay. Except for the first generation, the effective reproduction number was estimated by generation, assisting evaluation of public health control programs.
Conclusions: The variance of the generation time is relatively limited compared with the mean for measles, and thus, the proposed model was able to identify the generation-dependent dynamics accurately during the early phase of the epidemic. Model comparison indicated the most likely number of generations, allowing us to assess how effective public health interventions would successfully prevent the secondary transmission.
Keywords: Forecasting; Measles.
Figures
References
-
- Darussalam B (2015) Cambodia, Japan verified as achieving measles elimination. Manila: World Health Organization Regional Office for the Western Pacific.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

