Muscarinic m2 receptor-mediated actin polymerization via PI3 kinase γ and integrin-linked kinase in gastric smooth muscle
- PMID: 30393912
- PMCID: PMC6347515
- DOI: 10.1111/nmo.13495
Muscarinic m2 receptor-mediated actin polymerization via PI3 kinase γ and integrin-linked kinase in gastric smooth muscle
Abstract
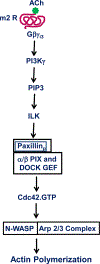
Background: Actin polymerization plays an important role in smooth muscle contraction. Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) was shown to mediate actin polymerization in airway smooth muscle. The role of ILK in actin polymerization in response to m2 receptor activation was not in gastric smooth muscle.
Methods: Phosphorylation of paxillin, neuronal Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASp), and association of paxillin with GEF proteins (Cool2/αPix [Cool2/PAK-interacting exchange factor alpha], Cool1/βPix [Cool1/PAK-interacting exchange factor beta], and DOCK 180 [Dedicator of cytokinesis]) and N-WASp with Arp2/3 complex were measured by western blot. Activation of Cdc42 was determined using an antibody for activated Cdc42. Actin polymerization was measured as an increase in F-actin/G-actin ratio.
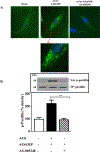
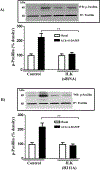
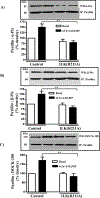
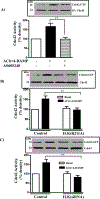
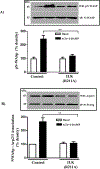
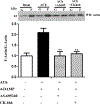
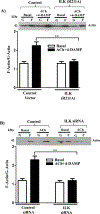
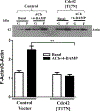
Results: Phosphorylation of paxillin, an association of paxillin with GEF proteins, Cdc42 activity, and actin polymerization were increased in response to m2 receptor activation in gastric smooth muscle cells. The increases in paxillin phosphorylation, Cdc42 activity, and actin polymerization were inhibited by a PI3Kγ inhibitor (AS-605240), ILK siRNA, and ILK dominant negative mutant (ILK [R211]). Increase in actin polymerization was also inhibited by Cdc42 dominant negative mutant (Cdc42 [T17N]). Increases in the association of paxillin with GEF proteins, phosphorylation of N-WASp and its association with Arp2/3 complex were inhibited by ILK (R211).
Conclusion: In gastric smooth muscle cells, activation of PI3Kγ by muscarinic m2 receptors causes ILK-dependent phosphorylation of paxillin, an association of paxillin with Cdc42 GEF proteins and activation of Cdc42, which, in turn, causes phosphorylation of N-WASp and its association with Arp2/3 complex leading to actin polymerization.
Keywords: ILK; PI3 Kinase; actin polymerization; m2 receptors; smooth muscle.
© 2018 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Murthy KS. Signaling for contraction and relaxation in smooth muscle of the gut. Annu Rev Physiol 2006; 68: 345–374. - PubMed
-
- Kamm KE, Stull JT. Dedicated myosin light chain kinases with diverse cellular functions. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 4527–4530 - PubMed
-
- Somlyo AP, Somlyo AV. Ca2+ sensitivity of smooth muscle and nonmuscle myosin II: modulated by G proteins, kinases, and myosin phosphatase. Physiol Rev 2003; 83: 1325–1358. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

