Survival, causes of death, and cardiovascular events in patients with Marfan syndrome
- PMID: 30393980
- PMCID: PMC6305663
- DOI: 10.1002/mgg3.489
Survival, causes of death, and cardiovascular events in patients with Marfan syndrome
Abstract
Background: To explore survival, causes of death, and the prevalence of cardiovascular events in a Norwegian Marfan syndrome (MFS) cohort. MFS is a heritable connective tissue disorder associated with reduced life expectancy-primarily due to aortic pathology.
Methods: A follow-up study of 84 MFS adults, initially investigated in 2003-2004. In 2014-2015, 16 were deceased, 47 of 68 survivors consented to new clinical investigations. Analyses of events were performed for 47 survivors and 16 deceased at follow-up. Standardized mortality ratios (SMR), using the mortality rate of the Norwegian population as reference, were calculated for all 84 and calculated for men and women separately. Causes of death and information on cardiovascular events were retrieved from death certificates and medical records.
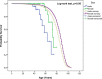
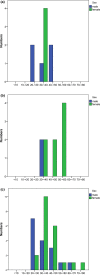
Results: Standardized mortality ratios (95% confidence interval): for the whole cohort: 5.24 (3.00-8.51); for men: 8.20 (3.54-16.16); for women: 3.85 (1.66-7.58). Cardiovascular causes were found in 11 of 16 deceased, eight of these related to aortic pathology. Cancer was the cause of death in three patients. At follow-up, 51% had new cardiovascular events; 59% had undergone aortic surgery. Men experienced aortic events at younger age than women. 32% of the survivors were not followed-up as recommended.
Conclusion: Life expectancy is reduced in this MFS cohort compared to the Norwegian population. Cardiovascular complications develop throughout life, particularly aortic pathology, the major cause of death in MFS. Death and aortic pathology seem to occur earlier in men. There is a need to improve follow-up according to guidelines.
Keywords: Marfan syndrome; aortic surgery; cardiovascular events; causes of death; survival.
© 2018 The Authors. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Erbel, R. , Aboyans, V. , Boileau, C. , Bossone, E. , Bartolomeo, R. D. , Eggebrecht, H. , … Vrints, C. J. (2014). 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of aortic diseases: Document covering acute and chronic aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult. The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal, 35(41), 2873–2926. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu281 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Faivre, L. , Collod‐Beroud, G. , Loeys, B. L. , Child, A. , Binquet, C. , Gautier, E. , … Boileau, C. (2007). Effect of mutation type and location on clinical outcome in 1,013 probands with Marfan syndrome or related phenotypes and FBN1 mutations: An international study. American Journal of Human Genetics, 81(3), 454–466. 10.1086/520125 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

