PLK1: a promising and previously unexplored target in double-hit lymphoma
- PMID: 30395539
- PMCID: PMC6264726
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI124919
PLK1: a promising and previously unexplored target in double-hit lymphoma
Abstract
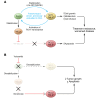
Inhibitors that target specific kinases or oncoproteins have become popular additions to or replacements for cytotoxic chemotherapies to treat many different types of cancer. However, many tumors lack a discernable target kinase and an amplified oncoprotein and/or rely on several cooperating mechanisms for progression. Thus, combinations of targeted therapies are essential for treating many cancers to avoid the rapid emergence of resistance. In this issue of the JCI, Ren et al. use an elegant kinase activity-profiling method and identify activity of the oncogene polo-like kinase-1 (PLK1) as an important driver of double-hit lymphoma (DHL), an aggressive subgroup of B cell lymphoma characterized by chromosomal translocations involving c-MYC and BCL2 or BCL6. Moreover, PLK1 activity was associated with MYC expression and poor prognosis in DHL patients. PLK1 inhibition with volasertib, alone and in combination with the BCL-2 inhibitor venetoclax, was efficacious in multiple DHL models, including mice harboring DHL patient-derived xenografts. Together, these data support PLK1 as a promising prognostic marker and therapeutic target for DHL.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Comment on
-
PLK1 stabilizes a MYC-dependent kinase network in aggressive B cell lymphomas.J Clin Invest. 2018 Dec 3;128(12):5517-5530. doi: 10.1172/JCI122533. Epub 2018 Nov 5. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 30260324 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
MYC/BCL2 double-hit high-grade B-cell lymphoma.Adv Anat Pathol. 2013 Sep;20(5):315-26. doi: 10.1097/PAP.0b013e3182a289f2. Adv Anat Pathol. 2013. PMID: 23939148 Review.
-
High-grade B-cell Lymphoma With MYC Rearrangement and Without BCL2 and BCL6 Rearrangements Is Associated With High P53 Expression and a Poor Prognosis.Am J Surg Pathol. 2016 Feb;40(2):253-61. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0000000000000542. Am J Surg Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26448193
-
MYC/BCL6 double-hit lymphoma (DHL): a tumour associated with an aggressive clinical course and poor prognosis.Histopathology. 2016 Jun;68(7):1090-8. doi: 10.1111/his.12884. Epub 2015 Dec 8. Histopathology. 2016. PMID: 26426741
-
The BET bromodomain inhibitor CPI203 overcomes resistance to ABT-199 (venetoclax) by downregulation of BFL-1/A1 in in vitro and in vivo models of MYC+/BCL2+ double hit lymphoma.Oncogene. 2018 Apr;37(14):1830-1844. doi: 10.1038/s41388-017-0111-1. Epub 2018 Jan 22. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29353886
-
MYC-associated and double-hit lymphomas: a review of pathobiology, prognosis, and therapeutic approaches.Cancer. 2014 Dec 15;120(24):3884-95. doi: 10.1002/cncr.28899. Epub 2014 Jul 24. Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25060588 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis, In Vitro and In Silico Anticancer Activity of New 4-Methylbenzamide Derivatives Containing 2,6-Substituted Purines as Potential Protein Kinases Inhibitors.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 25;22(23):12738. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312738. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884546 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Molecular Mechanisms and Drugs for Aconitine-Induced Cardiotoxicity in Zebrafish through RNA Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis.Med Sci Monit. 2020 Jun 29;26:e924092. doi: 10.12659/MSM.924092. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32598336 Free PMC article.
-
The role of aurora A and polo-like kinases in high-risk lymphomas.Blood Adv. 2019 Jun 11;3(11):1778-1787. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000232. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 31186254 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Affinity enhancement of polo-like kinase 1 polo box domain-binding ligands by a bivalent approach using a covalent kinase-binding component.RSC Chem Biol. 2024 Jun 4;5(8):721-728. doi: 10.1039/d4cb00031e. eCollection 2024 Jul 31. RSC Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 39092437 Free PMC article.
-
Dual-target inhibitors of bromodomain and extra-terminal proteins in cancer: A review from medicinal chemistry perspectives.Med Res Rev. 2022 Mar;42(2):710-743. doi: 10.1002/med.21859. Epub 2021 Oct 11. Med Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 34633088 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

