Laboratory assays on the effects of a novel acaricide, SYP-9625 on Tetranychus cinnabarinus (Boisduval) and its natural enemy, Neoseiulus californicus (McGregor)
- PMID: 30395569
- PMCID: PMC6218021
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199269
Laboratory assays on the effects of a novel acaricide, SYP-9625 on Tetranychus cinnabarinus (Boisduval) and its natural enemy, Neoseiulus californicus (McGregor)
Abstract
Objective: Tetranychus cinnabarinus (Boisduval) is an agricultural mite pest threatens crops throughout the world, causing serious economic loses. Exploring the effects of acaricides on predatory mites is crucial for the combination of biological and chemical control of T. cinnabarinus. Neoseiulus californicus (McGregor) is one of the principal natural enemies of T. cinnabarinus, which can be applied in protected agriculture. In this study, the effects of sublethal concentrations of a new acaricide, SYP-9625 on two mite species, and the effects of the application concentration on predatory mite, N. californicus were assessed. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the effect of SYP-9625 on life parameters and predation capacity of N. californicus based on the concentration-response bioassay of T. cinnabarinus to explor the application of the new acaricide with natural enemy N. californicus.
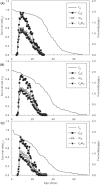
Method: All of the experiments were conducted under laboratory conditions [25 ± 1°C, 16: 8 h (L: D) and 75 ± 5% RH]. The sublethal concentrations LC10 (0.375μg/mL) and the LC30 (0.841μg/mL) against T. cinnabarinus and the application concentration (100μg/mL) against N. californicus were used to evaluate the effects of SYP-9625 on population parameters of N. californicus based on an age-stage, two-sex life table and its predation capacity by functional response.
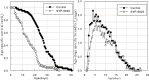
Result: cinnabarinus females treated with LC30 exhibited significantly reduced net reproductive rates (R0 = 11.02) in their offspring compared with females treated with LC10 (R0 = 14.96) and untreated females (R0 = 32.74). However, the intrinsic rate of increase (rm) and the finite rate of increase (λ) of N. californicus indicated that the application concentration of SYP-9625 had no significant negative effect on N. californicus eggs (rm = 0.277, λ = 1.319) compared to the control (rm = 0.292, λ = 1.338). Additionally, most population parameters of N. californicus showed a dose-dependent manner with the increase of the concentration of SYP-9625 against T. cinnabarinus. SYP-9625 also stimulated the control efficiency of N. californicus against immobile stages including eggs and larvae.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that sublethal concentrations of SYP-9625 can inhibit the population growth of T. cinnabarinus. In addition, the sublethal concentrations and the application concentration showed no effect on the population growth of N. californicus. These two advantages described above showed great commercial potential of this new acaricide based on population parameters of the two mite species and predation capacity of the predatory mite under laboratory conditions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Sublethal effects of chlorfenapyr and acequinocyl on the functional and numerical responses of the predatory mites Phytoseiulus persimilis and Neoseiulus californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) feeding on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae).Exp Appl Acarol. 2024 Dec 30;94(1):20. doi: 10.1007/s10493-024-00984-7. Exp Appl Acarol. 2024. PMID: 39739142
-
How does Neoseiulus californicus McGregor respond to sublethal doses of entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana (Hyp.: Cordycipitaceae)?Bull Entomol Res. 2024 Oct;114(5):598-605. doi: 10.1017/S0007485324000397. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Bull Entomol Res. 2024. PMID: 39328185
-
Lethal and sublethal effects of carlina oxide on Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) and Neoseiulus californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae).Pest Manag Sci. 2024 Mar;80(3):967-977. doi: 10.1002/ps.7827. Epub 2023 Nov 1. Pest Manag Sci. 2024. PMID: 37822147
-
Management of Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae) in strawberry fields with Neoseiulus californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and acaricides.Exp Appl Acarol. 2007;42(2):107-20. doi: 10.1007/s10493-007-9081-2. Epub 2007 Jun 5. Exp Appl Acarol. 2007. PMID: 17549586
-
Meta-analysis and review of pesticide non-target effects on phytoseiids, key biological control agents.Pest Manag Sci. 2021 Nov;77(11):4848-4862. doi: 10.1002/ps.6531. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Pest Manag Sci. 2021. PMID: 34169634 Review.
Cited by
-
Increasing Cyetpyrafen Spray Volume and Ozone Spray Improves the Control Effects against Two-Spotted Spider Mite (Tetranychus urticae) in Strawberries.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jun 28;13(13):1792. doi: 10.3390/plants13131792. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38999632 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral response of Panonychus citri (McGregor) (Acari: Tetranychidae) to synthetic chemicals and oils.PeerJ. 2021 Apr 5;9:e10899. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10899. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33868798 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular cloning and functional verification of chalcone synthase genes from cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) in defense against Tetranychus cinnabarinus infestation.PLoS One. 2025 Apr 24;20(4):e0321276. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0321276. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40273040 Free PMC article.
-
Toxicity and Control Efficacy of an Organosilicone to the Two-Spotted Spider Mite Tetranychus urticae and Its Crop Hosts.Insects. 2022 Mar 30;13(4):341. doi: 10.3390/insects13040341. Insects. 2022. PMID: 35447783 Free PMC article.
-
Acaricidal Activity and Field Efficacy Analysis of the Potential Biocontrol Agent Bacillus vallismortis NBIF-001 against Spider Mites.Microorganisms. 2022 Aug 30;10(9):1750. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10091750. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36144351 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dejan M, Pantelija P, Slobodan M. Acaricides-biological profiles, effects and used in modern crop protection 2011. 39–62 p.
-
- Yu H, Cheng Y, Xu M, Song Y, Luo Y, Li B. Synthesis, Acaricidal Activity and Structure−Activity Relationships of Pyrazolyl Acrylonitrile Derivatives. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry. 2016; 51. - PubMed
-
- Alinejad M, Kheradmand K, Fathipour Y. Sublethal effects of fenazaquin on life table parameters of the predatory mite Amblyseius swirskii (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol. 2014; 3: 361–373. - PubMed
-
- Poletti M, Maia A, Omoto C. Toxicity of neonicotinoid insecticides to Neoseiulus californicus and Phytoseiulus macropilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and their impact on functional response to Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Biological Control. 2007; 1: 30–36.
-
- Hamedi N, Fathipour Y, Saber M. Sublethal effects of abamectin on the biological performance of the predatory mite, Phytoseius plumifer (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Exp Appl Acarol. 2011; 1: 29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

