Data-driven, voxel-based analysis of brain PET images: Application of PCA and LASSO methods to visualize and quantify patterns of neurodegeneration
- PMID: 30395576
- PMCID: PMC6218048
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206607
Data-driven, voxel-based analysis of brain PET images: Application of PCA and LASSO methods to visualize and quantify patterns of neurodegeneration
Abstract
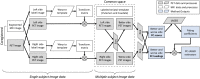
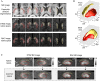
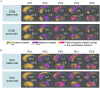
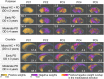
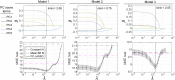
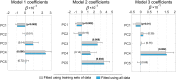
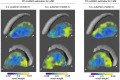
Spatial patterns of radiotracer binding in positron emission tomography (PET) images may convey information related to the disease topology. However, this information is not captured by the standard PET image analysis that quantifies the mean radiotracer uptake within a region of interest (ROI). On the other hand, spatial analyses that use more advanced radiomic features may be difficult to interpret. Here we propose an alternative data-driven, voxel-based approach to spatial pattern analysis in brain PET, which can be easily interpreted. We apply principal component analysis (PCA) to identify voxel covariance patterns, and optimally combine several patterns using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO). The resulting models predict clinical disease metrics from raw voxel values, allowing for inclusion of clinical covariates. The analysis is performed on high-resolution PET images from healthy controls and subjects affected by Parkinson's disease (PD), acquired with a pre-synaptic and a post-synaptic dopaminergic PET tracer. We demonstrate that PCA identifies robust and tracer-specific binding patterns in sub-cortical brain structures; the patterns evolve as a function of disease progression. Principal component LASSO (PC-LASSO) models of clinical disease metrics achieve higher predictive accuracy compared to the mean tracer binding ratio (BR) alone: the cross-validated test mean squared error of adjusted disease duration (motor impairment score) was 16.3 ± 0.17 years2 (9.7 ± 0.15) with mean BR, versus 14.4 ± 0.18 years2 (8.9 ± 0.16) with PC-LASSO. We interpret the best-performing PC-LASSO models in the spatial sense and discuss them with reference to the PD pathology and somatotopic organization of the striatum. PC-LASSO is thus shown to be a useful method to analyze clinically-relevant tracer binding patterns, and to construct interpretable, imaging-based predictive models of clinical metrics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Novel spatial analysis method for PET images using 3D moment invariants: applications to Parkinson's disease.Neuroimage. 2013 Mar;68:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.11.055. Epub 2012 Dec 11. Neuroimage. 2013. PMID: 23246861
-
Novel data-driven, equation-free method captures spatio-temporal patterns of neurodegeneration in Parkinson's disease: Application of dynamic mode decomposition to PET.Neuroimage Clin. 2020;25:102150. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.102150. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Neuroimage Clin. 2020. PMID: 31901793 Free PMC article.
-
Spectral guided sparse inverse covariance estimation of metabolic networks in Parkinson's disease.Neuroimage. 2021 Feb 1;226:117568. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117568. Epub 2020 Nov 25. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 33246128 Free PMC article.
-
Human Positron Emission Tomography Neuroimaging.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2019 Jun 4;21:551-581. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-062117-121056. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2019. PMID: 31167104 Review.
-
Examining similarity structure: multidimensional scaling and related approaches in neuroimaging.Comput Math Methods Med. 2013;2013:796183. doi: 10.1155/2013/796183. Epub 2013 Apr 15. Comput Math Methods Med. 2013. PMID: 23662162 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Classifying migraine using PET compressive big data analytics of brain's μ-opioid and D2/D3 dopamine neurotransmission.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 13;14:1173596. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1173596. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37383727 Free PMC article.
-
A Random Forest Model for Predicting Social Functional Improvement in Chinese Patients with Schizophrenia After 3 Months of Atypical Antipsychotic Monopharmacy: A Cohort Study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021 Mar 19;17:847-857. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S280757. eCollection 2021. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021. PMID: 33776440 Free PMC article.
-
Regional SUV quantification in hybrid PET/MR, a comparison of two atlas-based automatic brain segmentation methods.EJNMMI Res. 2020 Jun 8;10(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13550-020-00648-8. EJNMMI Res. 2020. PMID: 32514906 Free PMC article.
-
An improved approach for fault detection by simultaneous overcoming of high-dimensionality, autocorrelation, and time-variability.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 17;15(12):e0243146. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243146. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33332390 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal patterns of putaminal dopamine processing in Parkinson's disease: A multi-tracer positron emission tomography study.Neuroimage Clin. 2022;36:103246. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103246. Epub 2022 Oct 25. Neuroimage Clin. 2022. PMID: 36451352 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

