Nanoparticulate matter exposure results in neuroinflammatory changes in the corpus callosum
- PMID: 30395590
- PMCID: PMC6218079
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0206934
Nanoparticulate matter exposure results in neuroinflammatory changes in the corpus callosum
Abstract
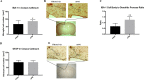
Epidemiological studies have established an association between air pollution particulate matter exposure (PM2.5) and neurocognitive decline. Experimental data suggest that microglia play an essential role in air pollution PM-induced neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. This study examined the effect of nano-sized particulate matter (nPM) on complement C5 deposition and microglial activation in the corpus callosum of mice (C57BL/6J males). nPM was collected in an urban Los Angeles region impacted by traffic emissions. Mice were exposed to 10 weeks of re-aerosolized nPM or filtered air for a cumulative 150 hours. nPM-exposed mice exhibited reactive microglia and 2-fold increased local deposition of complement C5/ C5α proteins and complement component C5a receptor 1 (CD88) in the corpus callosum. However, serum C5 levels did not differ between nPM and filtered air cohorts. These findings demonstrate white matter C5 deposition and microglial activation secondary to nPM exposure. The C5 upregulation appears to be localized to the brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Calderón-Garcidueñas L, de la Monte SM. Apolipoprotein E4, Gender, Body Mass Index, Inflammation, Insulin Resistance, and Air Pollution Interactions: Recipe for Alzheimer’s Disease Development in Mexico City Young Females. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2017;58(3):613–30. 10.3233/JAD-161299 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wellenius GA, Boyle LD, Coull BA, Milberg WP, Gryparis A, Schwartz J, et al. Residential proximity to nearest major roadway and cognitive function in community-dwelling seniors: results from the MOBILIZE Boston Study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012;60(11):2075–80. 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2012.04195.x - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

