Association between helminth infections and diabetes mellitus in adults from the Lao People's Democratic Republic: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 30396368
- PMCID: PMC6219195
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-018-0488-2
Association between helminth infections and diabetes mellitus in adults from the Lao People's Democratic Republic: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: As a result of epidemiological transition, the health systems of low- and middle-income countries are increasingly faced with a dual disease burden of infectious diseases and emerging non-communicable diseases. Little is known about the mutual influence of these two disease groups. The aim of this study was to investigate the co-occurrence of helminth infections and diabetes mellitus in adults in Lao People's Democratic Republic (Lao PDR).
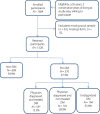
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study among 1600 randomly selected adults aged 35 and older from four different socio-economical and ecological provinces. Information on socio-demographics, risk factors and health conditions was obtained from personal interviews. Clinical assessments including anthropometry (height, weight, waist and hip circumference) and blood pressure measurements were also conducted. Diabetes was classified based on self-reported diagnoses and a point-of-care glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) test from finger prick blood samples. Stool samples for helminth diagnosis were examined with formalin-ether concentration technique for intestinal parasitic infections. The independent associations of helminth infections with diabetic status and HbA1c were assessed using multiple regression analyses.
Results: The prevalence of pre-diabetes and diabetes was 37.3% and 22.8%, respectively. Fifty-six percent of diabetic cases were undiagnosed and 85% of diagnosed diabetic cases had poor glycemic control. Participants from rural areas and from southern parts of the country had higher infection rates, with Opisthorchis viverrini, being the most common helminth infection (30.5%). We found a positive association between Taenia spp. infections and HbA1c (β = 0.117; 95% CI: 0.042-0.200) and diabetes mellitus risk (OR = 2.98; 95% CI: 1.10-8.05). No other helminth species was associated with glycated hemoglobin.
Conclusions: Hyperglycaemia and diabetic rates in Lao PDR are alarmingly high, but consistent with other high rates in the region. Given the high rates of under-diagnosis and poorly-controlled glycaemia in diabetes mellitus patients, routine diabetes screening and treatment is essential for the local healthcare system. Large longitudinal cohorts integrating biomarkers are warranted in the search of causal diabetes mellitus risk factors in the region. Common intestinal helminth infections, including O. viverrini, are unlikely to explain the high diabetes mellitus rates observed.
Keywords: Adults; Cross-sectional; Diabetes mellitus; Dual burden of disease; Epidemiology; Lao PDR; Opisthorchis viverrini; Taenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The National Ethics Committee for Health Research (NECHR) of the Ministry of Health (MoH) of Lao PDR (approval No. 017 NIOPH/NECHR, 14 March 2016) approved the study protocol. After research aim, methods, risks and benefits of the study were explained in detail to participants, district and provincial health authorities, written informed consent was also obtained from each participant prior data collection. Diagnosed helminth infection was treated according to the national treatment guidelines.
Consent for publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- IDF. International Diabetes Foundation. Diabetes Atlas - 8th edition. http://diabetesatlas.org/resources/2017-atlas.html. Accessed 25 Feb 2018.
-
- WHO World Health Organization. Soil-transmitted helminth infections. http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/soil-transmitted-helmint.... Accessed 21 Nov 2017.
-
- Soukhathammavong PA, Sayasone S, Phongluxa K, Xayaseng V, Utzinger J, Vounatsou P, et al. Low efficacy of single-dose albendazole and mebendazole against hookworm and effect on concomitant helminth infection in Lao PDR. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2012;6(1):e1417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0001417. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vonghachack Y, Odermatt P, Taisayyavong K, Phounsavath S, Akkhavong K, Sayasone S. Transmission of Opisthorchis viverrini, Schistosoma mekongi and soil-transmitted helminthes on the Mekong Islands Southern Lao PDR. Infect Dis Poverty. 2017;6(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s40249-017-0343-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

