Recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein drives regulatory macrophage polarization
- PMID: 30396910
- PMCID: PMC6234359
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018024497
Recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein drives regulatory macrophage polarization
Abstract
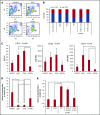
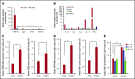
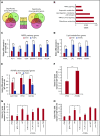
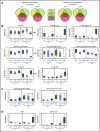
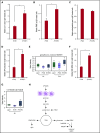
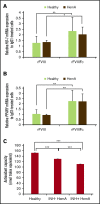
The main complication of replacement therapy with factor in hemophilia A (HemA) is the formation of inhibitors (neutralizing anti-factor VIII [FVIII] antibodies) in ∼30% of severe HemA patients. Because these inhibitors render replacement FVIII treatment essentially ineffective, preventing or eliminating them is of top priority in disease management. The extended half-life recombinant FVIII Fc fusion protein (rFVIIIFc) is an approved therapy for HemA patients. In addition, it has been reported that rFVIIIFc may induce tolerance to FVIII more readily than FVIII alone in HemA patients that have developed inhibitors. Given that the immunoglobulin G1 Fc region has the potential to interact with immune cells expressing Fc receptors (FcRs) and thereby affect the immune response to rFVIII, we investigated how human macrophages, expressing both FcRs and receptors reported to bind FVIII, respond to rFVIIIFc. We show herein that rFVIIIFc, but not rFVIII, uniquely skews macrophages toward an alternatively activated regulatory phenotype. rFVIIIFc initiates signaling events that result in morphological changes, as well as a specific gene expression and metabolic profile that is characteristic of the regulatory type Mox/M2-like macrophages. Further, these changes are dependent on rFVIIIFc-FcR interactions. Our findings elucidate mechanisms of potential immunomodulatory properties of rFVIIIFc.
© 2018 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: K.K.-T., G.M.R., A.S., J.D., R.T.P., J.S., and C.L. are or were employees of Bioverativ, a Sanofi company. K.L.H. is an employee of Biogen.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Factor VIII-Fc Activates Natural Killer Cells via Fc-Mediated Interactions With CD16.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 28;12:692157. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.692157. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34262568 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and prolonged activity of recombinant factor VIII Fc fusion protein in hemophilia A patients.Blood. 2012 Mar 29;119(13):3031-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-09-382846. Epub 2012 Jan 5. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22223821 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Prolonged activity of a recombinant factor VIII-Fc fusion protein in hemophilia A mice and dogs.Blood. 2012 Mar 29;119(13):3024-30. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-08-367813. Epub 2012 Jan 13. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22246033 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging benefits of Fc fusion technology in the context of recombinant factor VIII replacement therapy.Haemophilia. 2020 Nov;26(6):958-965. doi: 10.1111/hae.14123. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Haemophilia. 2020. PMID: 32885562 Free PMC article. Review.
-
rFVIIIFC for hemophilia A prophylaxis.Expert Rev Hematol. 2018 Dec;11(12):937-943. doi: 10.1080/17474086.2018.1549478. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Expert Rev Hematol. 2018. PMID: 30449223 Review.
Cited by
-
The Neonatal Fc Receptor (FcRn): A Misnomer?Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 10;10:1540. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01540. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31354709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recombinant Factor VIII Fc Inhibits B Cell Activation via Engagement of the FcγRIIB Receptor.Front Immunol. 2020 Feb 7;11:138. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00138. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32117285 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling Atherosclerotic Plaque Heterogeneity and SPP1+/VCAN+ Macrophage Subtype Prognostic Significance Through Integrative Single-Cell and Bulk-Seq Analysis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Apr 23;17:2399-2426. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S454505. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38681071 Free PMC article.
-
First study of extended half-life rFVIIIFc in previously untreated patients with hemophilia A: PUPs A-LONG final results.Blood. 2022 Jun 30;139(26):3699-3707. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021013563. Blood. 2022. PMID: 35421219 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Factor VIII Fc Fusion Protein but not FVIII Drives Human Monocyte-Derived Dendritic Cell Activation via FcγRIIa.Hemasphere. 2020 Jan 3;4(1):e330. doi: 10.1097/HS9.0000000000000330. eCollection 2020 Feb. Hemasphere. 2020. PMID: 32072146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Manco-Johnson MJ, Abshire TC, Shapiro AD, et al. . Prophylaxis versus episodic treatment to prevent joint disease in boys with severe hemophilia. N Engl J Med. 2007;357(6):535-544. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava A, Brewer AK, Mauser-Bunschoten EP, et al. ; Treatment Guidelines Working Group on Behalf of The World Federation of Hemophilia. Guidelines for the management of hemophilia. Haemophilia. 2013;19(1):e1-e47. - PubMed
-
- Gouw SC, van der Bom JG, Ljung R, et al. ; PedNet and RODIN Study Group. Factor VIII products and inhibitor development in severe hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(3):231-239. - PubMed
-
- Benson G, Auerswald G, Elezović I, et al. . Immune tolerance induction in patients with severe hemophilia with inhibitors: expert panel views and recommendations for clinical practice. Eur J Haematol. 2012;88(5):371-379. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

