Whole-Genome Sequencing for Predicting Clarithromycin Resistance in Mycobacterium abscessus
- PMID: 30397069
- PMCID: PMC6325232
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01204-18
Whole-Genome Sequencing for Predicting Clarithromycin Resistance in Mycobacterium abscessus
Abstract
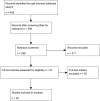
Mycobacterium abscessus is emerging as an important pathogen in chronic lung diseases, with concern regarding patient-to-patient transmission. The recent introduction of routine whole-genome sequencing (WGS) as a replacement for existing reference techniques in England provides an opportunity to characterize the genetic determinants of resistance. We conducted a systematic review to catalogue all known resistance-determining mutations. This knowledge was used to construct a predictive algorithm based on mutations in the erm(41) and rrl genes which was tested on a collection of 203 sequentially acquired clinical isolates for which there were paired genotype/phenotype data. A search for novel resistance-determining mutations was conducted using a heuristic algorithm. The sensitivity of existing knowledge for predicting resistance in clarithromycin was 95% (95% confidence interval [CI], 89 to 98%), and the specificity was 66% (95% CI, 54 to 76%). The subspecies alone was a poor predictor of resistance to clarithromycin. Eight potential new resistance-conferring single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) were identified. WGS demonstrated probable resistance-determining SNPs in regions that the NTM-DR line probe cannot detect. These mutations are potentially clinically important, as they all occurred in samples that were predicted to be inducibly resistant and for which a macrolide would therefore currently be indicated. We were unable to explain all resistance, raising the possibility of the involvement of other as yet unidentified genes.
Keywords: macrolides; nontuberculous mycobacteria; whole-genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
References
-
- Prevots DR, Shaw PA, Strickland D, Jackson LA, Raebel MA, Blosky MA, Montes de Oca R, Shea YR, Seitz AE, Holland SM, Olivier KN. 2010. Nontuberculous mycobacterial lung disease prevalence at four integrated health care delivery systems. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 182:970–976. doi:10.1164/rccm.201002-0310OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bryant JM, Grogono DM, Greaves D, Foweraker J, Roddick I, Inns T, Reacher M, Haworth CS, Curran MD, Harris SR, Peacock SJ, Parkhill J, Floto RA. 2013. Whole-genome sequencing to identify transmission of Mycobacterium abscessus between patients with cystic fibrosis: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet 381:1551–1560. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60632-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bryant JM, Grogono DM, Rodriguez-Rincon D, Everall I, Brown KP, Moreno P, Verma D, Hill E, Drijkoningen J, Gilligan P, Esther CR, Noone PG, Giddings O, Bell SC, Thomson R, Wainwright CE, Coulter C, Pandey S, Wood ME, Stockwell RE, Ramsay KA, Sherrard LJ, Kidd TJ, Jabbour N, Johnson GR, Knibbs LD, Morawska L, Sly PD, Jones A, Bilton D, Laurenson I, Ruddy M, Bourke S, Bowler IC, Chapman SJ, Clayton A, Cullen M, Daniels T, Dempsey O, Denton M, Desai M, Drew RJ, Edenborough F, Evans J, Folb J, Humphrey H, Isalska B, Jensen-Fangel S, Jönsson B, Jones AM, et al. 2016. Emergence and spread of a human-transmissible multidrug-resistant nontuberculous mycobacterium. Science 354:751–757. doi:10.1126/science.aaf8156. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harris KA, Underwood A, Kenna DTD, Brooks A, Kavaliunaite E, Kapatai G, Tewolde R, Aurora P, Dixon G. 2014. Whole-genome sequencing and epidemiological analysis do not provide evidence for cross-transmission of Mycobacterium abscessus in a cohort of pediatric cystic fibrosis patients. Clin Infect Dis 60:1007–1016. doi:10.1093/cid/ciu967. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

